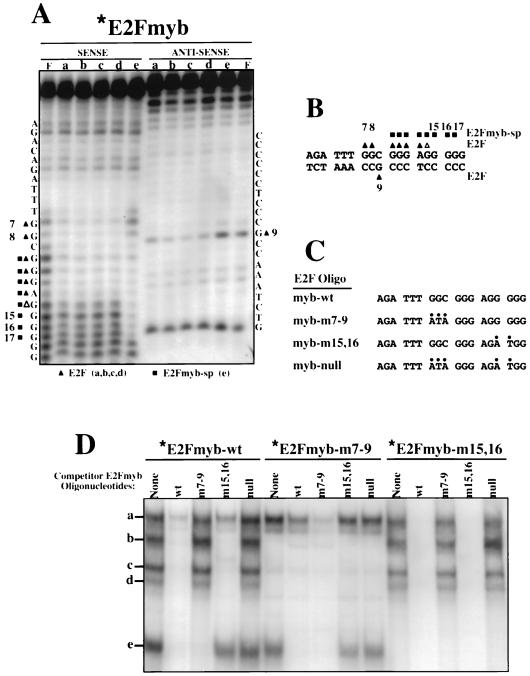
FIG. 5.
E2Fmyb-sp and E2F complexes interact with overlapping DNA sequences. (A) Methylation interference analysis of complexes a to e was performed with X50-7 nuclear extracts and the E2Fmyb probe. Sequences of the sense and antisense strands are indicated adjacent to the gels. Triangles and squares indicate bases whose methylation completely (filled) or partially (empty) blocked formation of complexes a to d (triangles) or e (squares). The cleavage pattern observed with an unbound probe (F) is also shown. (B) Summary of methylation interference analysis shown in panel A. (C) Sequence of wild-type and mutant E2Fmyb probes. For each mutant, alterations relative to the wild-type sequences are indicated by dots. (D) EMSA analysis of complexes formed between X50-7 nuclear factors and radiolabeled E2Fmyb-wt, E2Fmyb-m7-9, and E2Fmyb-m15,16 probes. Reaction mixtures were incubated in the absence (None) or in the presence of a 100-fold excess of the indicated unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides. Positions of complexes a to e are marked.