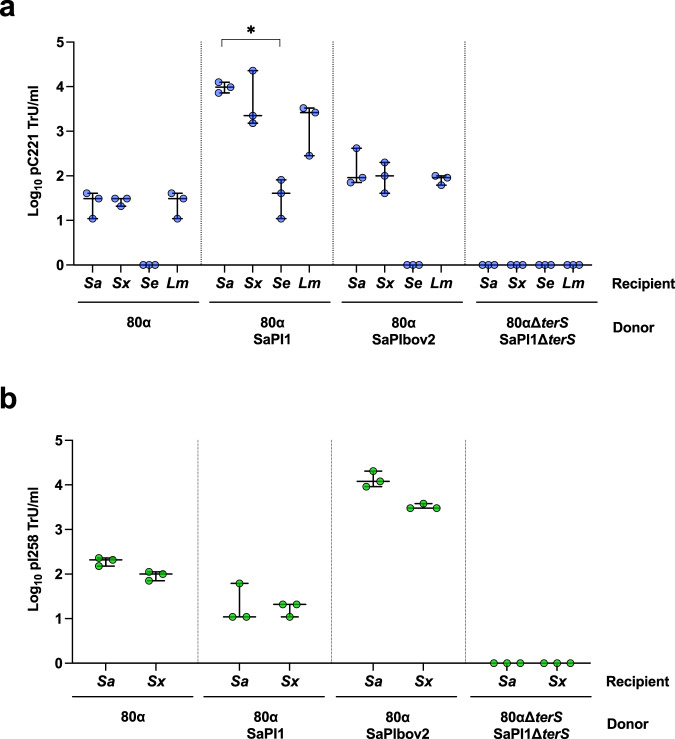
Fig. 5. Intra- and intergeneric transfer of pC221 and pI258.
RN4220 strains lysogenic for phage 80α (WT or mutant in small terminase) with SaPI1 (WT or mutant in small terminase) or SaPIbov2 (WT), carrying plasmids a pC221 (4.6 kb; blue circles) or b pI258 (29 kb; green circles) were induced with ciprofloxacin at 0.6 µg/ml to produce lysates. Log10 transductants (TrU) per ml were determined for each plasmid in different recipient strains: S. aureus RN4220 (Sa), S. xylosus (Sx), S. epidermidis (Se), and L. monocytogenes (Lm) for plasmid pC221, and S. aureus RN4220 (Sa), and S. xylosus (Sx) for pI258 (as this plasmid does not replicate in S. epidermidis or L. monocytogenes). All data is the result of three independent experiments (n = 3). Data for each donor strain are represented as boxplots where the middle line (bold) is the median, the lower and upper hinges correspond to the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers extend from the minimum to maximum values, with all individual data points shown as coloured circles. For a, Kruskal–Wallis (one-way ANOVA on ranks) with Dunn’s multiple comparison tests compared mean rank values between S. aureus and each recipient strain within each donor group. Asterisks denote significant p values: a *p = 0.0001; all other values were not statistically significant. For b Mann–Whitney tests (two-tailed) compared rank values between S. aureus and S. xylosus within each donor group. No statistically significant differences were observed (p > 0.05).