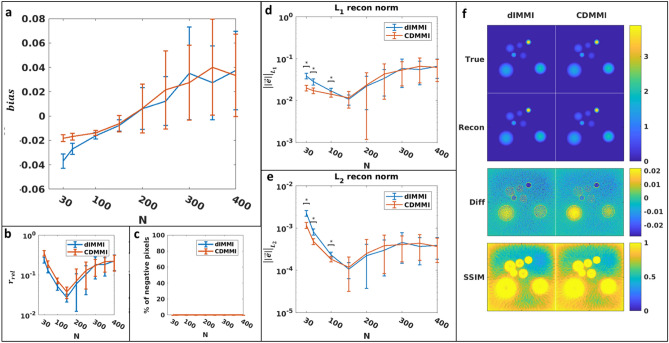
Figure 5.
Comparison of dIMMI- and CDMMI-based reconstructions using the nnAPCG reconstruction algorithm. (a) Both models tend towards increasing absolute error as a function of image size though (b) the relative residual for CDMMI is higher than dIMMI for low image resolutions, converging at higher resolutions. (c) Neither model incurs negative pixels due to the non-negative constraint. When considering the reconstruction L1 norm (d) and L2 norm (e) for each model, CDMMI results in a lower norm at low resolutions; again, both methods perform similarly at high resolutions. (f) depicts the ground truth, reconstructed, difference, and SSIM images for each of the methods. Both models underestimate the true image intensity for high-intensity objects when reconstructed using nnAPCG, causing mismatches towards the center of each object. Figure created using a combination of MATLAB and Microsoft PowerPoint.