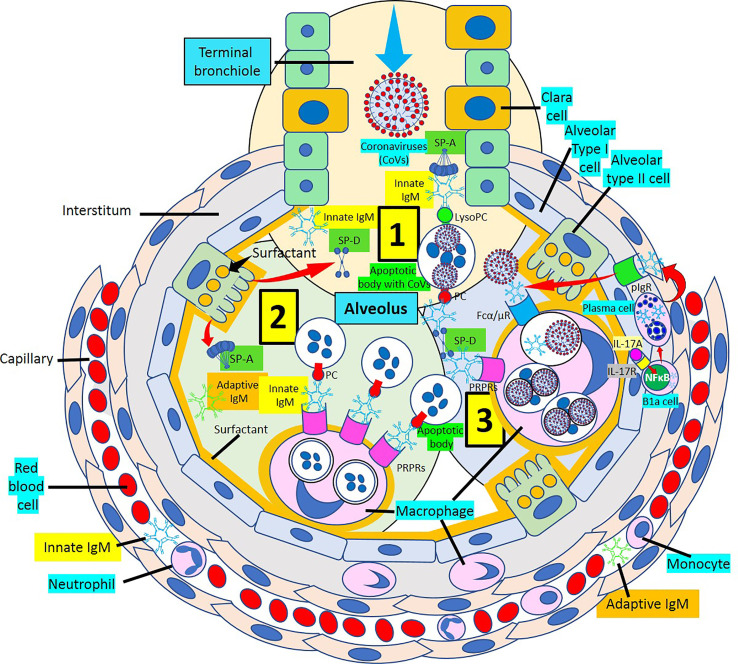
Figure 10.
Alveolus showing IgM response to coronavirus infection. [1] The arrival of coronaviruses into the alveolus generates an immediate IgM response mediated by innate and adaptive IgM antibodies. The IgM response in association with surfactant proteins D and A (SP-D and SP-A) facilitate virus neutralization and virus-infected apoptotic cell removal. [2] Innate and adaptive IgM participate in the macrophage-mediated removal of alveolar apoptotic cells through pattern recognition protein receptors (PRPRs) avoiding inflammation. [3] Virus-infected apoptotic cells are phagocytosed with the help of SP-D and SP-A through PRPRs. Recruitment of B1a cells into the alveolar wall under the stimulation of interleukin (IL)-17A via IL-17 receptor (IL-17R) and nuclear factor (NF) κB activation generate plasma cells that release IgM into the wall that is transported to the alveolus via polymeric immunoglobulin receptors (pIgRs). Viral particles bind IgM and are phagocytosed via Fcα/μ receptors (Fcα/μRs). lysoPC, lysophosphatidylcholine.