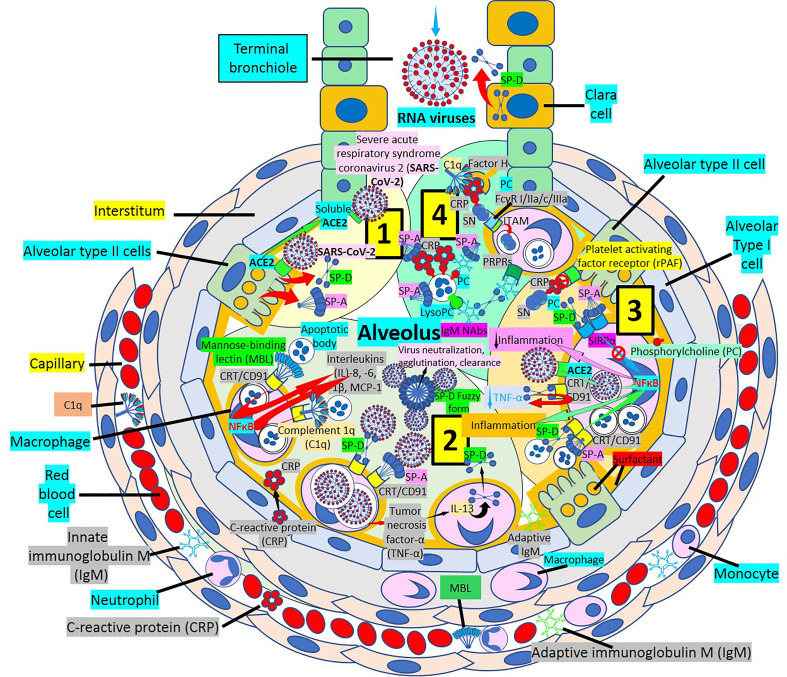
Figure 3.
Alveolar surfactant protein innate immune response to RNA viruses. [1] Intra-alveolar RNA viruses are exposed to surfactant proteins (SP)-A and -D produced by alveolar type II (AII) and Clara cells. SARS-CoV-2 binds ACE2 receptors in AII cells releasing soluble ACE2 to protect AII cells against SARS-CoV-2 infection. [2] MBL and C1q bind calreticulin/CD91 (CRT/CD91) receptors enhancing apoptotic body macrophage uptake and nuclear factor κB (NFκB)-mediated intra-alveolar release of IL-1ß, -6, -8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). CRT/CD91 bound SP-A and SP-D facilitate virus phagocytosis. TNF-α release stimulates IL-13-mediated SP-D macrophage output; and SP-D fuzzy form contributes to virus neutralization, agglutination and clearance. Circulating innate and adaptive IgM, MBL, C1q and CRP; and alveolar type I cell CRP synthesis and release contribute to alveolar immune defense. [3] CRT/CD91-bound SP-A and SP-D facilitate apoptosis and activate NFκB-mediated inflammation. Macrophage ACE2 facilitates virus uptake and SP-D-CRT/CD91 binding reduces TNF-α release. Signal inhibitory regulatory protein α (SIRPα) SP-A and SP-D binding inhibits inflammation. Native CRP blocks PC-mediated attachment of streptococcus pneumoniae (SN) to rPAF on alveolar epithelial cells. PC is a main component of alveolar surfactant. [4] Interaction of SP-A, SP-D, CRP and IgM natural antibodies (NAbs) with apoptotic cells facilitate macrophage uptake through pattern recognition protein receptors (PRPRs). CRP bound to C1q and factor H mediates SN uptake via Fcγ receptors and cytoplasmic immuno-tyrosine activating motif (ITAM) activation.