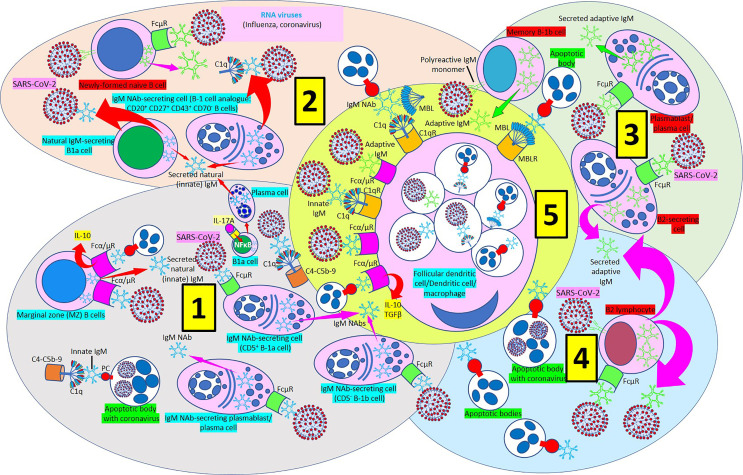
Figure 9.
IgM-mediated immune response in coronavirus infection. [1] Most of natural (innate) immunoglobulin M (IgM) natural antibodies (NAbs) are secreted by B-1 cells (CD5+ B-1a and CD5- B1b) without previous exposure to any antigen or pathogen. B-1a cells are critical in early protection during influenza infections through their IL-17A-driven differentiation into high-rate natural IgM producing plasma cells. Marginal zone (MZ) B cells can recognize IgM NAbs bound to RNA viruses and apoptotic cells through Fcα/μ receptors (Rs) and enhance interleukin-10 (IL-10) release. Innate IgM Nab-secreting cells (CD5+ B-1a and CD5- B1b cells; plasmablasts/plasma cells) recognize virus-bound IgM NAbs through membrane FcμRs. Innate IgM NAbs facilitate lysis of viruses and virus-infected apoptotic cells through activation of the complement cascade (C1q-C5b-9). [2] Natural IgM-secreting B1a cells and human B1 cells, identified in the umbilical cord and in adult peripheral blood and expressing the novel CD20+CD27+CD43+CD70- phenotype contribute to natural (innate) IgM secretion. Polyreactive IgM monomers on B cells (newly formed naïve B-cells, memory B1b cells) bind repetitive antigenic determinants on bacteria and viruses and induce immune (adaptive) antibody production without the involvement of T-cells. [3] Immune (adaptive) IgM are produced by adaptive B2 cells following exposure to an antigen or pathogen. B2-secreting cells and plasmablasts/plasma cells can produce immune IgM following antibody recognition by FcμRs. [4] B2 lymphocytes can secrete adaptive IgM antibodies following virus recognition by membrane IgM monomers and FcμR recognition of virus bound IgM. [5] Follicular dendritic cells, dendritic cells and macrophages can phagocytose viruses and apoptotic cells bound to innate or adaptive IgM through Fcα/μRs and C1qRs and enhance IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF) ß release to reduce inflammation.