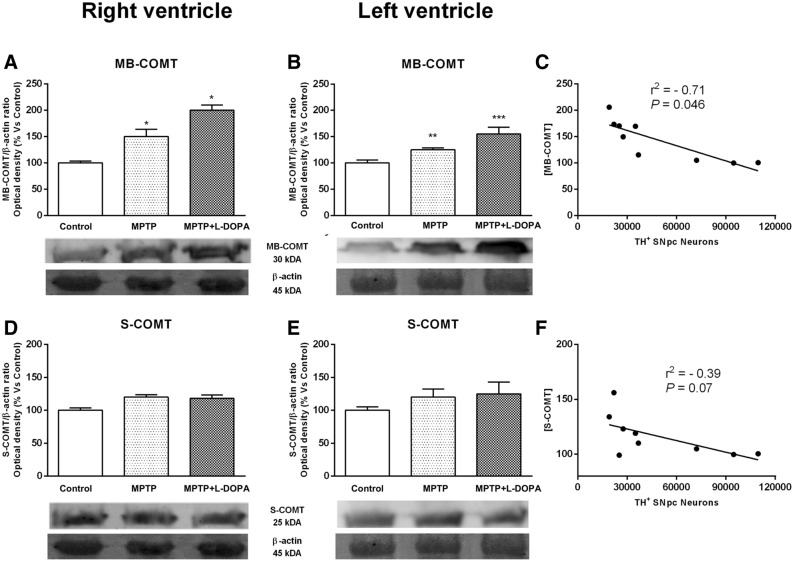
Figure 4.
Effects of MPTP and L-DOPA treatment on COMT in the monkey heart. (A, B) MB-COMT/β-actin ratio (optical density, % vs control) in controls, MPTP-treated monkeys and in the MPTP + L-DOPA group. MB-COMT expression was increased in the RV of MPTP- and MPTP + L-DOPA-treated animals compared to control group. (C) Significant correlation between MB-COMT and TH+ neurons in the SNpc (r2 = 0.71, P = 0.0046). (D, E) S-COMT/β-actin ratio (optical density, % vs control) in controls, MPTP-treated monkeys and in the MPTP + L-DOPA group. The quantitative analysis showed no differences between groups. (F) No correlation between S-COMT and TH+ neurons in the SNpc was observed. Data were compared by one-way ANOVA (MB-COMT: F(2,9) = 14.41, P = 0.0016, RV; F(2,9) = 11.62, P = 0.0032, LV. S-COMT: F(2,9) = 3.31, P = 0.0827, RV; F(2,9) = 1.742, P = 0.2293, LV) followed by Newman–Keuls post-hoc test. Values are represented as mean ± standard deviation. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control group). MB membrane, S soluble, COMT catechol-O-methyl transferase, MPTP 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, L-DOPA levodopa. (n = 4 animals/group and 2 technical replicates/animal).