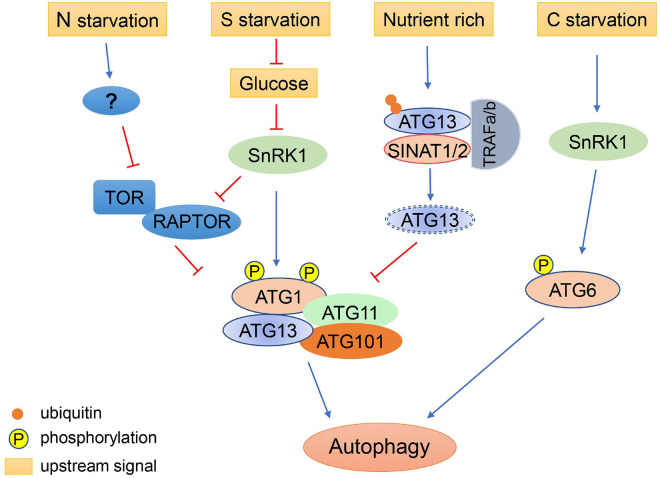
FIGURE 2.
Regulation of autophagy initiation under different nutritional conditions. Autophagy is induced by nitrogen (N) starvation in plants through inhibition of TOR. Sulfur (S) starvation regulates autophagy through the repression of glucose signaling, resulting in the activation of SnRK1, which inhibits TOR and activates the ATG1 autophagy initiation complex. Under nutrient-rich conditions, ATG13 is ubiquitinated by the SINATs-TRAF1s complex and degraded via the proteasome pathway, maintaining low levels of autophagy. Under prolonged carbon (C) starvation, ATG6 can be phosphorylated by SnRK1 to initiate autophagy via an ATG1-independent pathway.