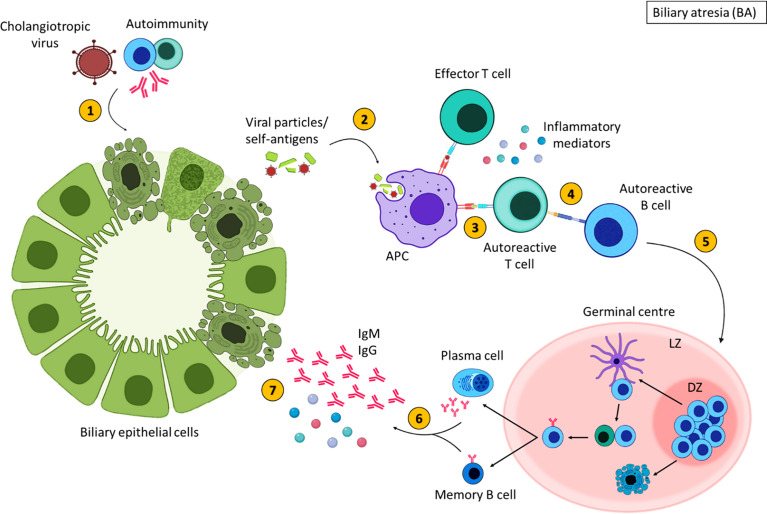
Figure 5.
Inflammatory-mediated damage in biliary atresia. In some children with BA, damage to the extrahepatic bile ducts may occur due to cholangiotropic viruses or autoimmunity (1), resulting in the expulsion of viral or self-antigens. These antigens are engulfed by antigen presenting cells (2) and presented to T cells (3). Autoreactive T cells that recognise self-antigens stimulate autoreactive B cells (4). Activated B cells then migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues and undergo germinal centres reactions (5) where B cells with increased affinity receptors differentiate into memory B cells and PCs (6). The secretion of inflammatory mediators and autoantibodies from memory B cells and PCs further damage BECs (7). Created with BioRender.com.