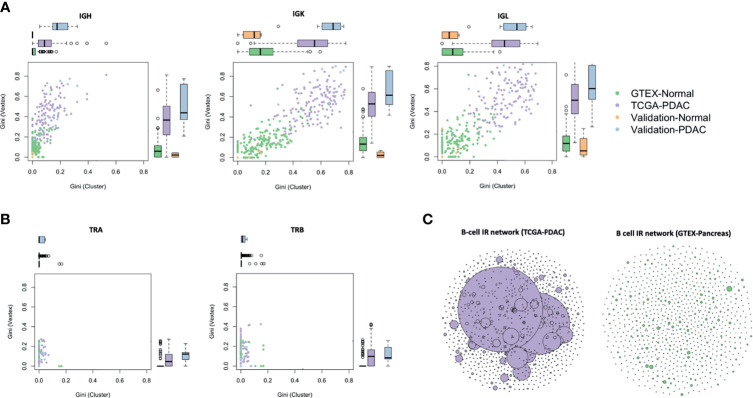
Figure 3.
Network analysis. Vertex Gini Index plotted against Cluster Gini Index for IGH, IGK, and IGL (A), and TRA and TRB (B). The scatter plot represents each sample. Boxplots show the Gini(V) and Gini(C) differences. p-values (TCGA vs. GTEx) − IGH: p (Gini(V) < 2.2 × 10−16, p (Gini(C) TCGA vs. GTEx) < 2.2 × 10−16; IGK: p (Gini(V) < 2.2 × 10−16, p (Gini(C) TCGA vs. GTEx) < 2.2 × 10−16; IGL: p (Gini(V) < 2.2 × 10−16, p (Gini(C) TCGA vs. GTEx) < 2.2 × 10−16. B-cell repertoire networks (C) from two samples representing one PDAC from TCGA (purple) and one normal pancreas from GTEx (green). Each vertex represents a unique BCR being the vertex size defined by the number of identical BCRs considering the nucleotide sequences. An edge exists between vertices when they belong to the same clone as defined before, so clusters are groups of interconnected vertices forming a clone.