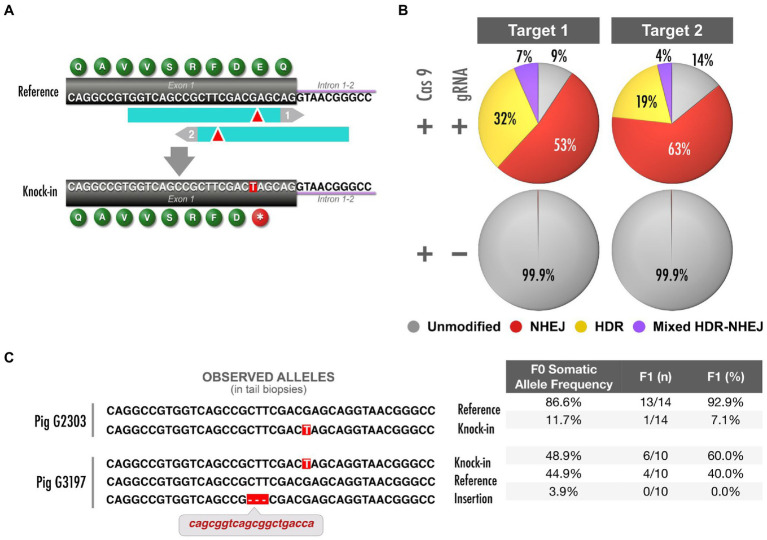
Figure 3.
NF1 early truncation model and analysis of mosaicism. (A) Top: schematic depicts NF1 exon 1 and two Cas9 target sites (blue, PAM in gray); donor oligonucleotides are not shown (Supplementary Table 3). Bottom: precise G>T mutation generates an early truncation codon. (B) In vitro validation of targets shown in (A). Quantification of DNA repair products through TAm-Seq of amplicons and CRISPResso analysis. (C) Of four founders in total, two representative, validated founders were bred to generate a herd of E19* F1 pigs. Left: allele sequences detected in somatic tail tissue from these founders (>1%). Right: Quantification of abundance of each allele and the proportion of sired F1 pigs that carry each allele from each founder. The pig with higher abundance of E19* in somatic tissue yielded a higher frequency of E19* offspring (logistic regression, p<0.005).