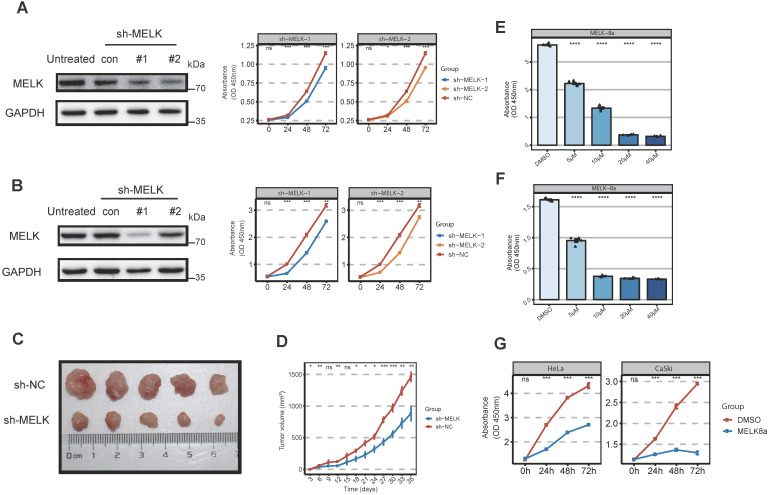
Figure 3.
MELK is essential for cervical cancer proliferation. A. Effect of MELK knockdown on cell growth. HeLa cells are stably transduced with short hairpin MELK(sh-MELK). Then use the CCK8 proliferation assay kit to detect the proliferation of HeLa cells under different treatments. * P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 and **** P <0.0001 compared to control. B. Effect of MELK knockdown on cell growth. CaSki cells are stably transduced with short hairpin MELK (sh-MELK). Then use the CCK8 proliferation assay kit to detect the proliferation of CaSki cells under different treatments. * P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 and **** P <0.0001 compared to control. C. MELK-knockdown HeLa cells were injected into nude mice, and the tumors were harvested. D. The volume of tumors was subsequently measured every 3 days (mean ± SD); * P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 and **** P <0.0001 compared to the shNC group. E and F. Viability of (G) HeLa and (H) CaSki cells 24 hours posttreatment with MELK-8A. Cell viability in a dose-dependent manner 24 hours posttreatment. DMSO was used as a control; * P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 and **** P <0.0001 compared to the DMSO group. G. Effect of MELK kinase activity on cell proliferation after 5μM MELK-8A inhibition. The cell viability of HeLa and CaSki cells treated with MELK-8A was measured every 24 hours for 72 hours using the CCK8 cell proliferation assay kit. * P <0.05, ** P <0.01, *** P <0.001 and **** P <0.0001 compared to the 0h group.