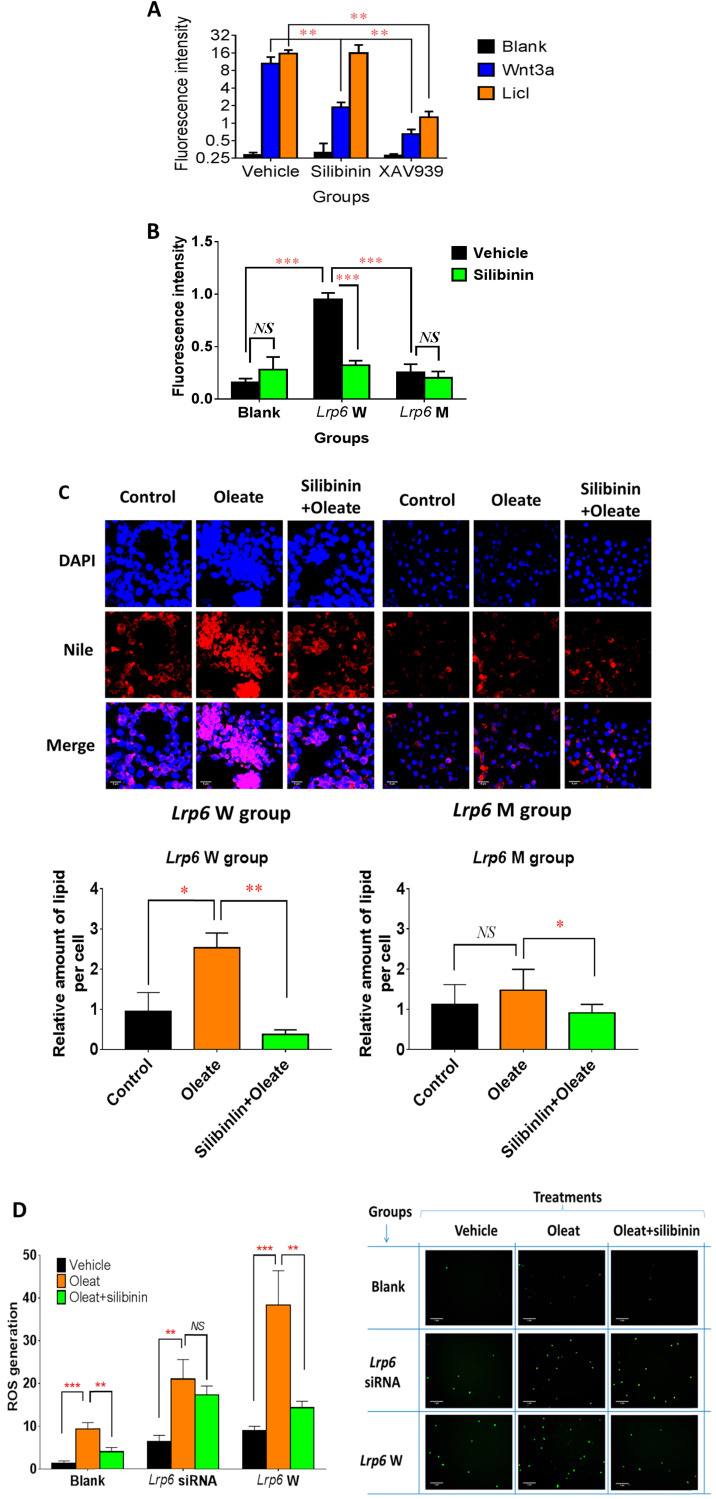
Figure 4.
Lrp6 was a target for silibinin to inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 signaling pathway and the generation of ROS. (A) Comparison of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity between the silibinin-treated and untreated HL7702 cells. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity was determined from the fluorescence intensity induced by LiCl treatment or Wnt3a-conditioned medium in reporter gene assays. XAV939, a characterized Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor, served as a positive control. (B) Comparison of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity between the silibinin-treated and untreated TOPFlash HEK293 cells overexpressing Lrp6 W (wide-type) or Lrp6 M (mutant). The Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity was determined by reporter gene assays for the TOPFlash cells, as described in Methods. (C) Comparison of the oleat uptake between the silibinin-treated and untreated HL7702 cells overexpressing Lrp6 W (wide-type) or Lrp6 M (mutant) (Scale bar, 5μM). (D) Comparison of ROS generation induced by oleat treatment between the silibinin-treated and untreated HL7702 cells transfected with Lrp6 siRNA or Lrp6 W vector (Scale bar, 1μM). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; NS, No significance.