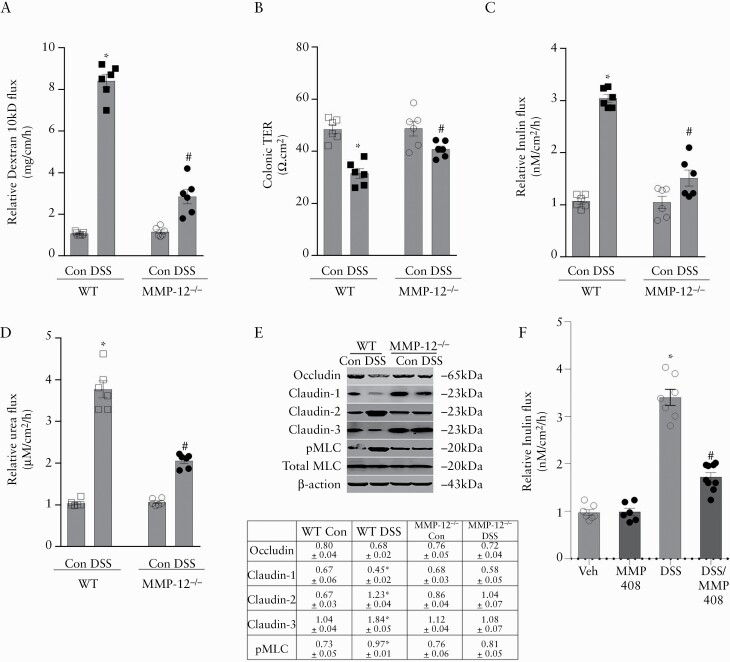
Figure 4.
Role of MMP-12 in colonic TJ barrier. A: In in-vivo colonic recycling perfusion, DSS colitis caused a multifold increase in Texas red-labelled dextran [10 kDa] flux in the colon of WT but not MMP-12-/- mice. B: In Ussing chamber studies, DSS-induced drop in the electrical resistance [TER] of colonic tissue was attenuated in MMP-12-/- mice. DSS-induced increase in colonic inulin [C] and urea [D] flux was attenuated in MMP-12-/- mice. * , #p < 0.01 versus WT control and each other, one-way ANOVA [Tukey’s multiple-comparison test]. E: Effect of DSS colitis on various TJ proteins. DSS-induced decrease in occludin, claudin-1, claudin-3, and pMLC was prevented in MMP-12-/- mice. The expression of pore-forming claudin-2 was increased in WT DSS but not MMP-12-/- DSS mice. Representation of three blots in each group. Densitometry for blots is shown in the table. Arbitrary values: occludin, claudin-1, -2, and -3 represent respective TJ protein expression normalised to β -actin. The pMLC values represent pMLC expression normalised to total MLC; *p < 0.05 versus WT control, one-way ANOVA [Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test]. F: MMP-12 inhibition with MMP408 attenuated DSS-induced increase in mouse colonic inulin flux. MMP408 [5 mg/kg] was administered orally in 0.5% methylcellulose solution for 3 days before studying the colonic permeability. #p < 0.01 versus other groups, one-way ANOVA [Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test]. DSS, dextran sodium sulphate; WT, wild-type; TJ, tight junction; ANOVA, analysis of variance; pMLC, phosphorylated myosin light chain.