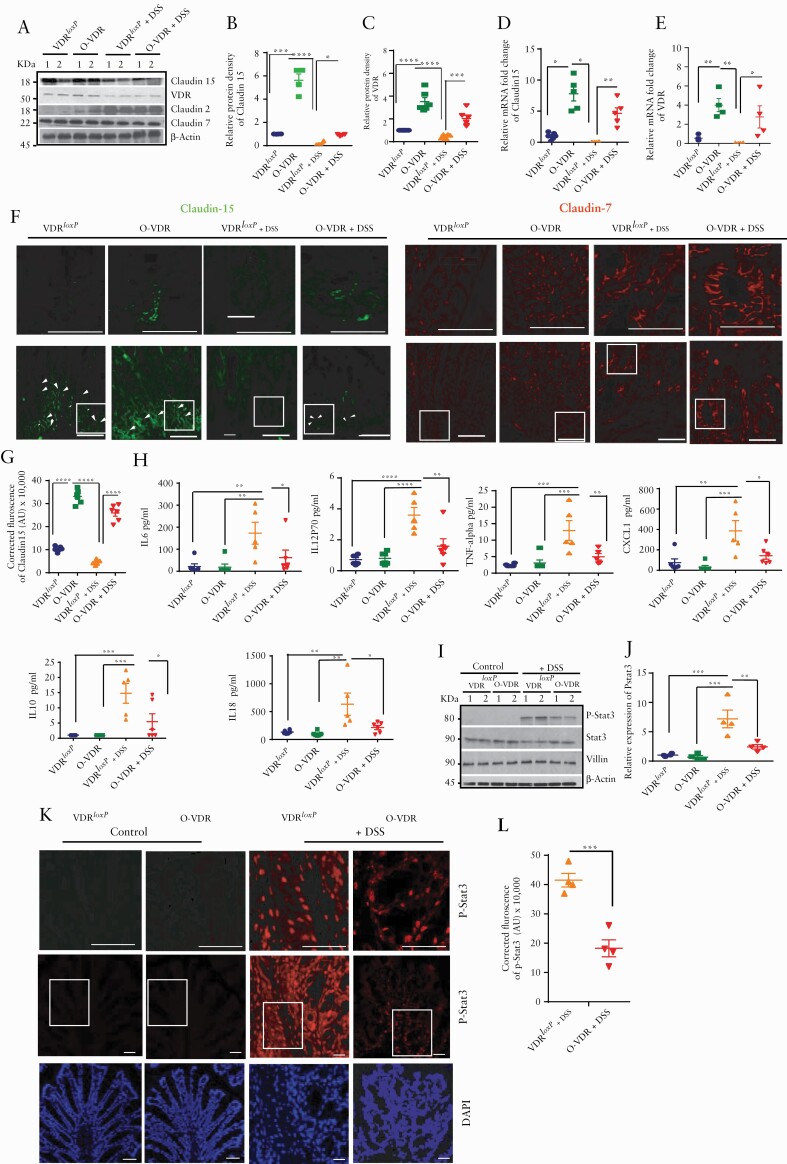
Figure 4.
O-VDR mice retained Claudin-15 expression following acute DSS colitis, thus protecting the host from inflammation. [A] Western blot analysis of mouse colonic tissue indicated decreased VDR and Claudin-15 protein expression following acute DSS colitis; however, Claudin-15 expression was restored in O-VDR mice. Densitometric analysis of [B] Claudin-15 and [C] VDR by western blot. Relative mRNA expression of [D] Claudin-15 and [E] VDR in mouse colonic epithelium. [F] The expression and distribution of Claudin-15 in mouse colonic epithelium is shown by green fluorescence. Nuclear staining is revealed by blue DAPI. [G] The intensity of the immunofluorescence staining of Claudin-15. [H] Cytokines were inhibited in DSS-treated O-VDR mice. [I] Western blot analysis indicating protein levels of p-stat 3, stat3, villin, and actin in VDRloxP and O-VDR mice. [J] Densitometric analysis of p-stat3 expression. [K] Immunofluorescence staining indicating p-stat3 expression and distribution in mouse colonic epithelium. Control VDRloxP and O-VDR mice did not show detectable p-stat3. [L] Quantification of the red fluorescence of p-stat3, n = 3–6. Data were analysed by unpaired t test or one-way ANOVA, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Scale bar = 50 µm, n = 3–6. . VDR, vitamin D receptor; ANOVA, analysis of variance.