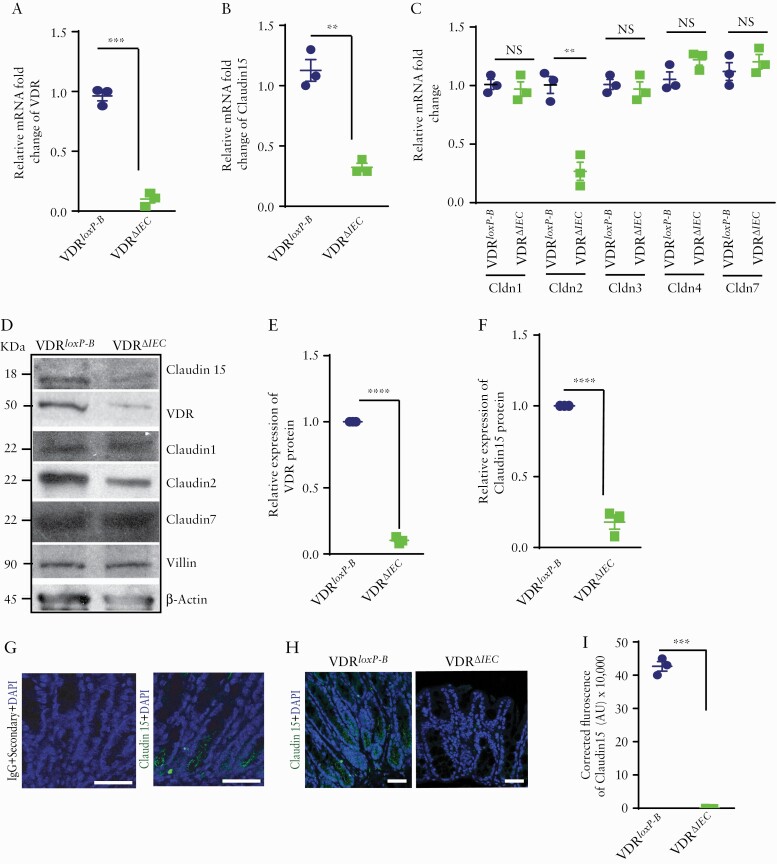
Figure 7.
Deletion of VDR reduced Claudin-15 expression in vivo. Reduced VDR and Claudin-15 were detected in VDRΔIEC mice as indicated by [A] VDR mRNA and [B] claudin-15 mRNA. However, mRNA of [C] Claudin-1, 3, 4, 7 was unaltered with exception of Claudin-2. [D] Western blot image showing decreased expressions of VDR, Claudin-15, and Claudin-2 in mouse colon. Densitometric quantification of the western blots of [E] VDR and [F] Claudin-15. [G] No staining was detected in the mice colon tissue section by IgG [+only secondary antibody] whereas similar section stained with Claudin-15 antibody indicated staining in the mice colon as indicated by specific green colour. [H] Representative images of ICC images indicating a lower level of Claudin-15 expression in mousee colon. [I] Quantification of the ICC staining. Scale bar = 50 µm. In each figure, values for the control group are indicated by blue colour and for the experimental group are indicated by light green colour; n = 3 for each group. VDRloxp-B: Belgium VDRloxp/loxp mice used in generating VDRΔIEC mice. Data were analysed by unpaired t test or one-way ANOVA, NS p > 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, and ****p ≤ 0.0001. VDR, vitamin D receptor; ICC, immunocytochemistry; ANOVA, analysis of variance; NS, non-significant.