Fig. 1.
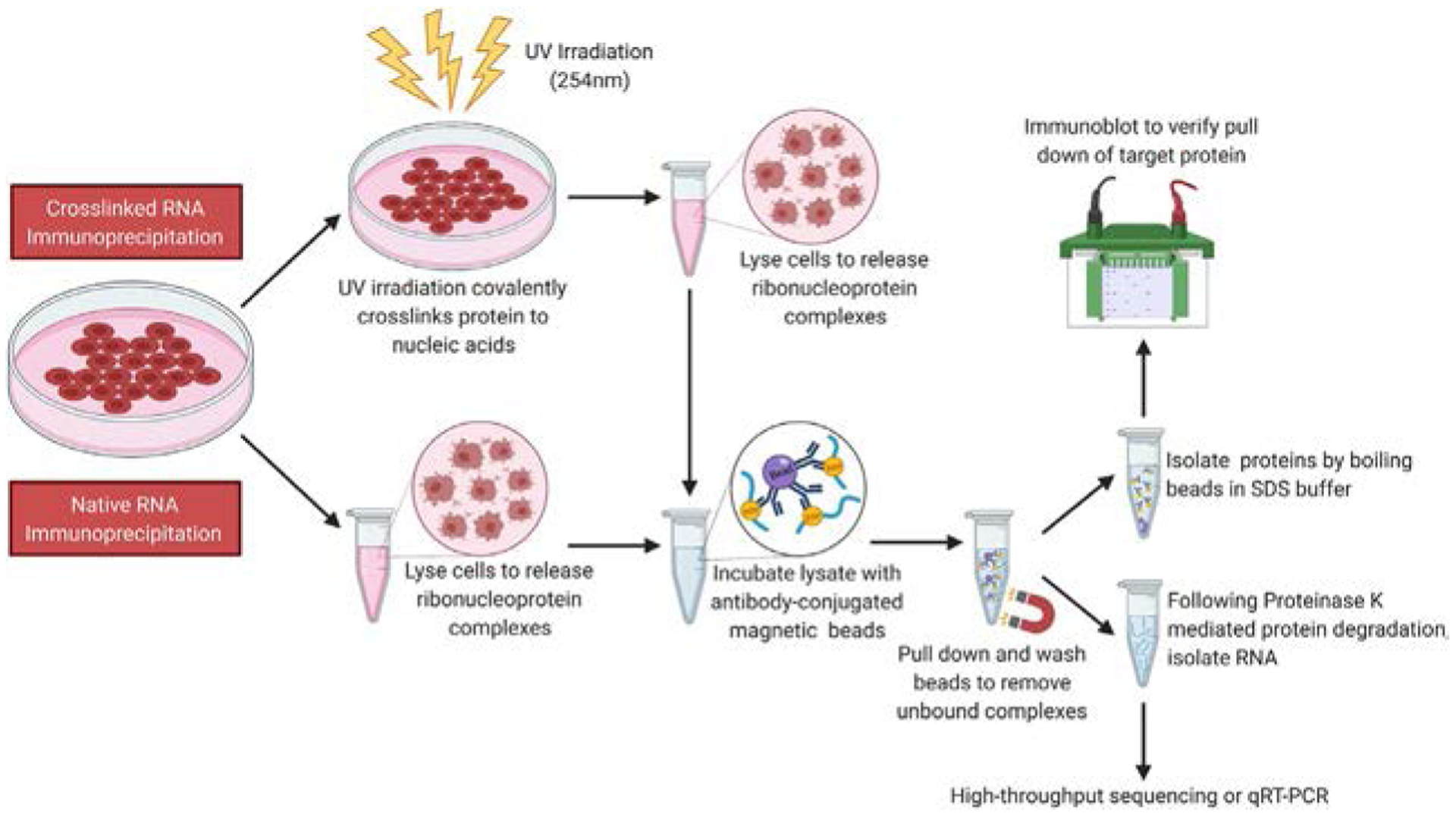
Schematic representation of a crosslinked and native RIP workflow. Cells (or other model organisms) can either be treated with a crosslinking agent that allows covalent crosslinking of proteins to bound RNA molecules (Crosslinked RIP) or not (Native RIP). Cells are lysed to release RBPs with bound RNAs, and the lysate is incubated with antibody-conjugated magnetic beads. Upon completion of incubation, beads are pulled down using a magnet and subjected to several rounds of stringent washing to remove nonspecific interactors. To examine immunoprecipitated protein, an SDS-containing buffer is added to the beads, and the mixture is boiled. The denatured protein lysate can then be resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane and subjected to immunoblotting. To isolate immunoprecipitated protein bound RNA, the beads can be treated with Proteinase K. Released RNA can be extracted using standard phenol-chloroform based techniques and used for qRT-PCR or high-throughput sequencing.
