Fig. 6. Formation of CX3CR1+ cytotoxic cells is ZEB2-dependent.
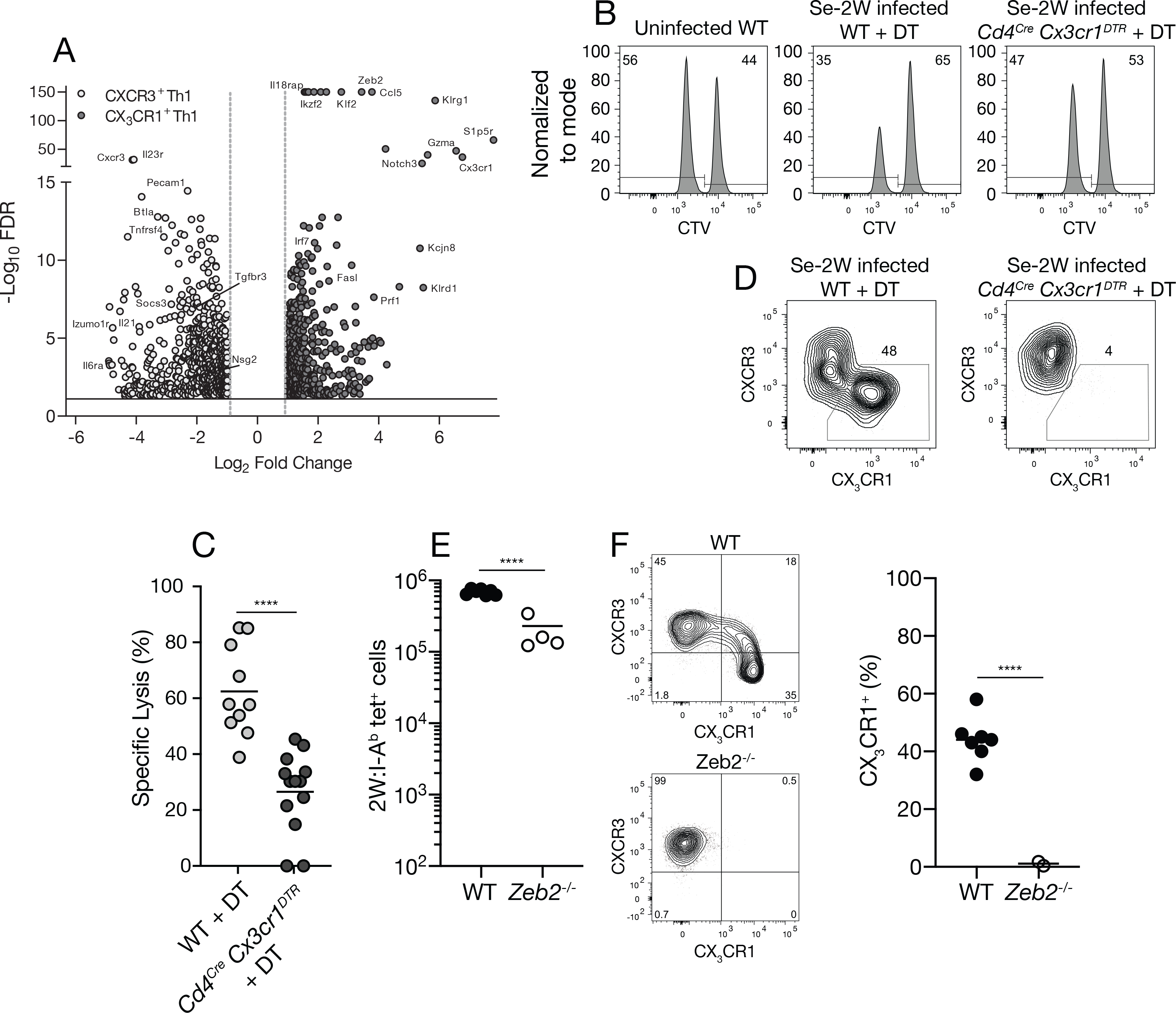
(A) Volcano plot of RNA sequencing results from LpdAp:I-Ab tetramer-binding CXCR3+ (open) or CX3CR1+ (closed) cells from day 30 Se-infected B6 × 129 F1 mice. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of an in vivo cytotoxicity assay using CTV to identify CTVlo splenic B cells pulsed with 2W peptide and CTVhi unpulsed B cells 20 hours after injection into the indicated mice. (C) Specific cell lysis of 2W peptide-pulsed B cells in individual mice (n ≥ 10 per group from three independent experiments) from the indicated groups. (D) Flow cytometry plots of T-bet+ 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding cells from day 30 Se-2W-infected mice from the indicated groups demonstrating depletion of CX3CR1+ cells from DT-treated Cd4Cre Cx3cr1DTR mice. (E) Number of 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding cells of wild-type (Zeb2fl/fl) or ZEB-deficient (Cd4cre Zeb2fl/fl) origin in day 10 Se-2W-infected chimeric mice. (F) Flow cytometry plots of T-bet+ 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding cells of wild-type (Zeb2fl/fl) or ZEB2-deficient (Cd4cre Zeb2fl/fl) origin in day 10 Se-2W-infected chimeric mice, with a scatter plot of the percent of CX3CR1+ cells among T-bet+ 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding cells. Values were compared using an unpaired Students t-test (****p < 0.0001) and were derived from two-three independent experiments. The horizontal lines represent the mean for each group.
