Fig. 7. Amplified Th1 cells provide superior protection from Se infection.
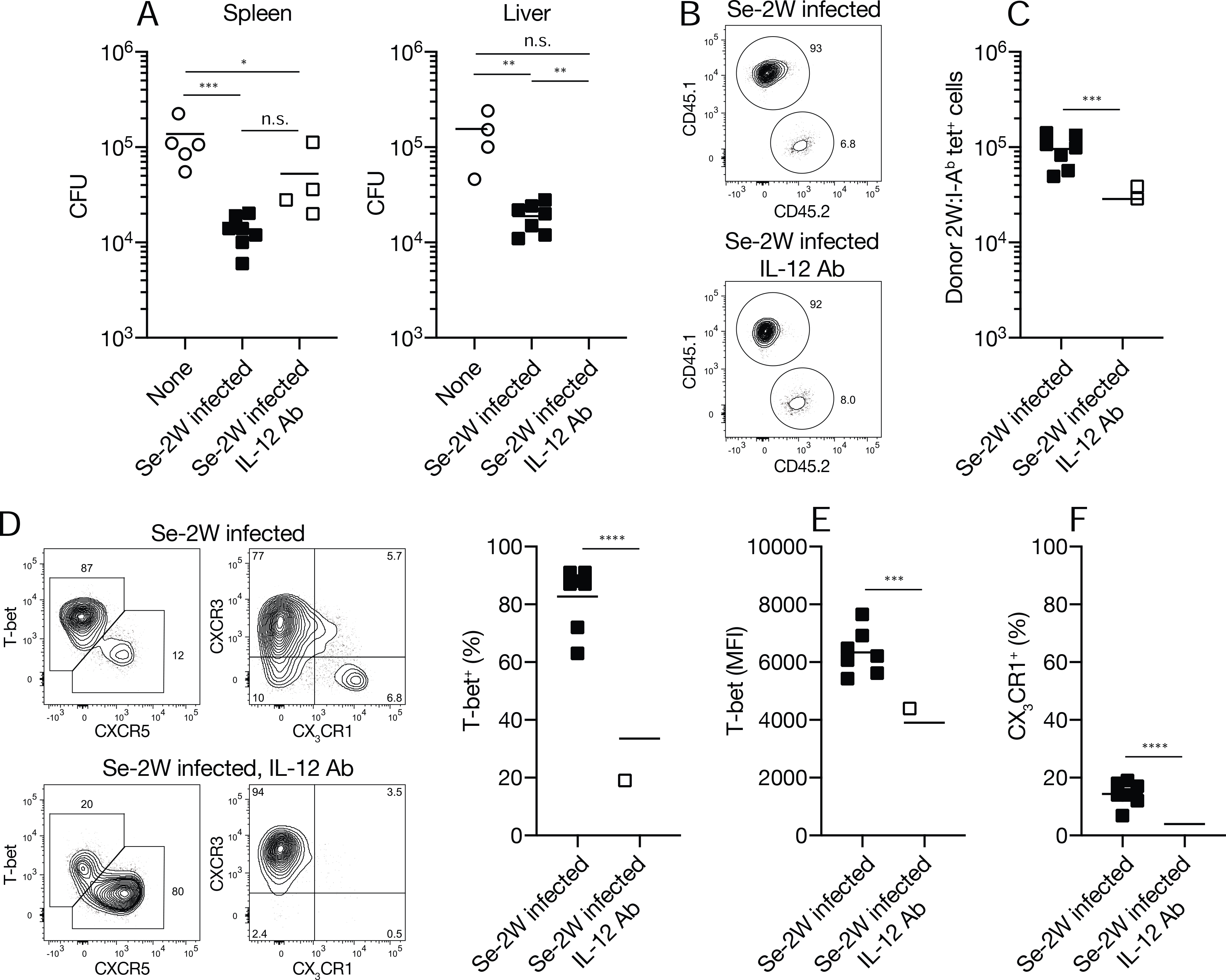
(A) CFU in the indicated organs from individual B6 mice (n = six per group from three independent experiments) that received CD4+ T cells from the indicated sources. (B) Flow cytometry plots used to identify 2W:I-Ab+ tetramer-binding T cells of donor (CD45.1) or recipient (CD45.2) origin in B6 mice that received CD4+ T cells from day seven Se-2W-infected (top) or IL-12 antibody-treated day seven Se-2W-infected mice (bottom). Some of the recipients of each type of donor T cell population were also treated with IL-12 antibody. IL-12 antibody treatment of the recipient mice had no discernable effect so the data for each donor population were pooled. (C) Number of 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding T cells from individual day seven Se-2W-infected (top) or IL-12 antibody-treated day seven Se-2W-infected mice (bottom) (n = six per group from three independent experiments) after three days in Se-2W-infected recipients. (D) Flow cytometry plots of 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding T cells from day seven Se-2W-infected or IL-12 antibody-treated day seven Se-2W-infected mice after three days in Se-2W-infected recipients, with scatter plots of percent T-bet+ cells. (E, F) Mean fluorescence intensity of T-bet+ cells (E) and percent CX3CR1+ cells (F) among T-bet+ 2W:I-Ab tetramer-binding from individual mice (n = six from three independent experiments). Values in A were compared using one-way ANOVA. Values in C-F were compared using an unpaired Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. Mean values on scatter plots are indicated with a horizontal bar.
