Figure 12 |.
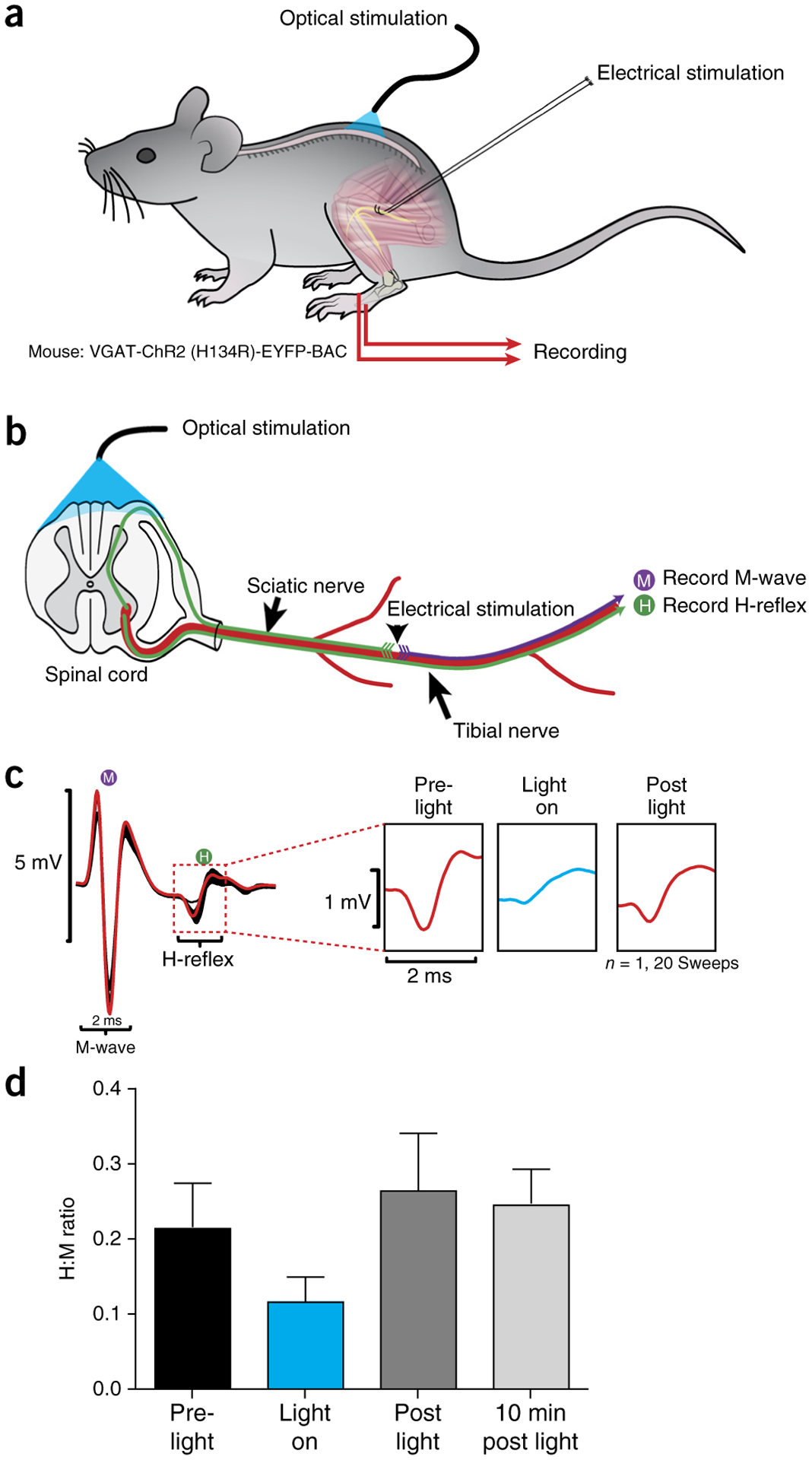
Photostimulation of the dorsal L4/L5 spinal cord reduces amplitude of monosynaptic reflex. (a) Schematic representation of stimulation and recording setup. (b) Electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve was performed on VGAT-ChR2 (H134R)-EYFP-BAC mice in the presence and absence of trains of photostimulation targeted toward VGAT neurons in the spinal cord. Photostimulation was accomplished using an array of six micro-LEDs in a flexible silicone bilayer, allowing stimulation of the surface of the spinal cord. (c) Example traces show a reduction in the H-reflex recorded from the flexor digitorum brevis (marked H in diagram) and expanded in right panels to show reduction in the H-reflex amplitude during light-on conditions. (d) Graph summarizing effects across conditions. Error bars refer to mean ± s.d. n = 20 for each bar. Local animal ethics committees approved these procedures. See REAGENTS section for details. Local ethics committees approved all procedures used to produce results shown here.
