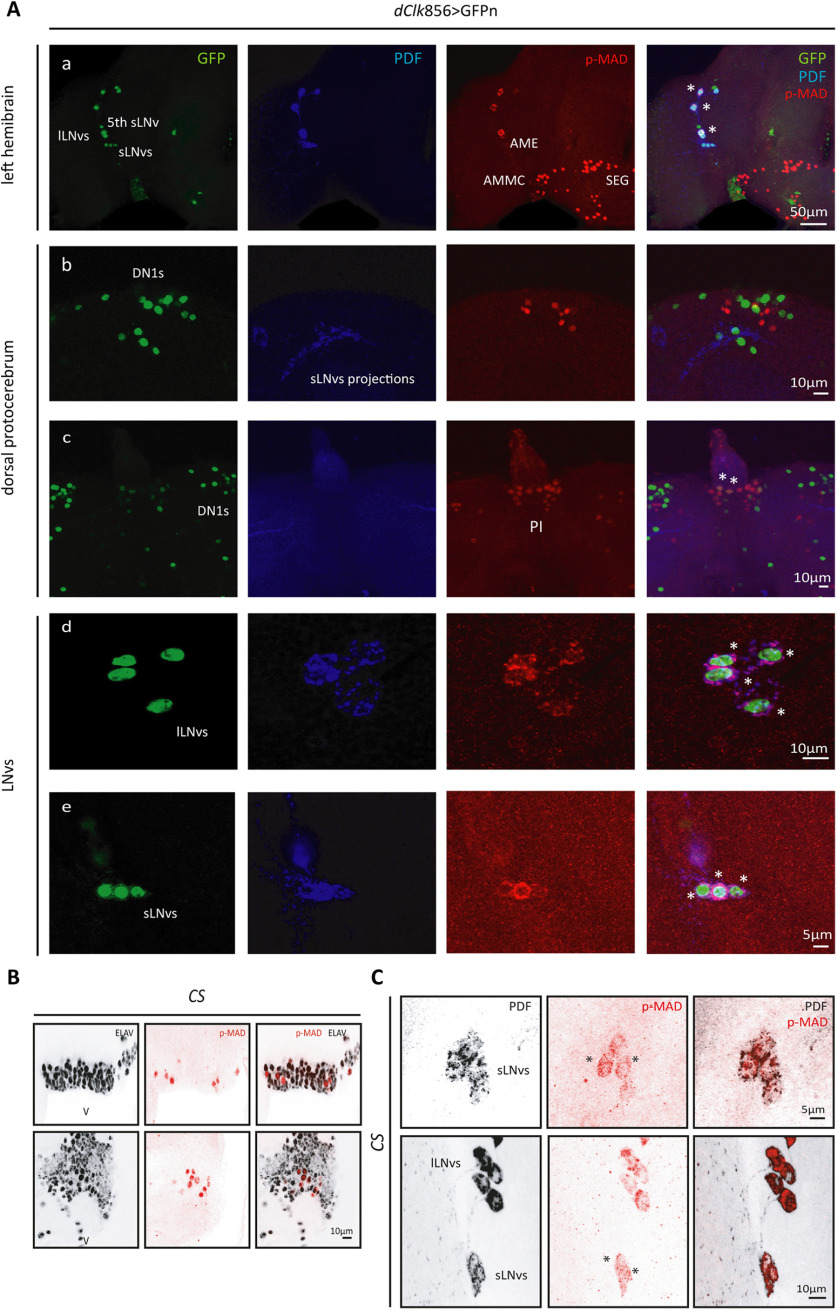
Figure 1.
The BMP pathway is active in the LNvs. Representative confocal images of different regions of the adult brain. A, Left hemibrain displaying the dorsal ventral part of the brain and LNvs (a). Dorsal protocerebrum, showing the DN1 cluster (b) and the PI (c). Detail of the lLNvs (d) and sLNvs (e). Nuclear GFPn staining (green) was used to identify the different circadian clusters driven by dClk856-G4, and PDF (blue) labels the LNvs; p-MAD (red) was used as a reporter of the activity of the BMP pathway. Asterisks denote colocalization of GFP and PDF (only in the LNvs) with p-MAD. B, Representative confocal images from ventral areas of the brain in wild-type (CS) flies. BMP pathway activation is reported by the detection of p-MAD (red) colocalized with the pan-neuronal marker ELAV (gray) at ZT02. C, Detection of nuclear p-MAD in the sLNvs at ZT1.5. LNvs were identified by PDF staining (gray). Asterisks highlight nuclear p-MAD signal.