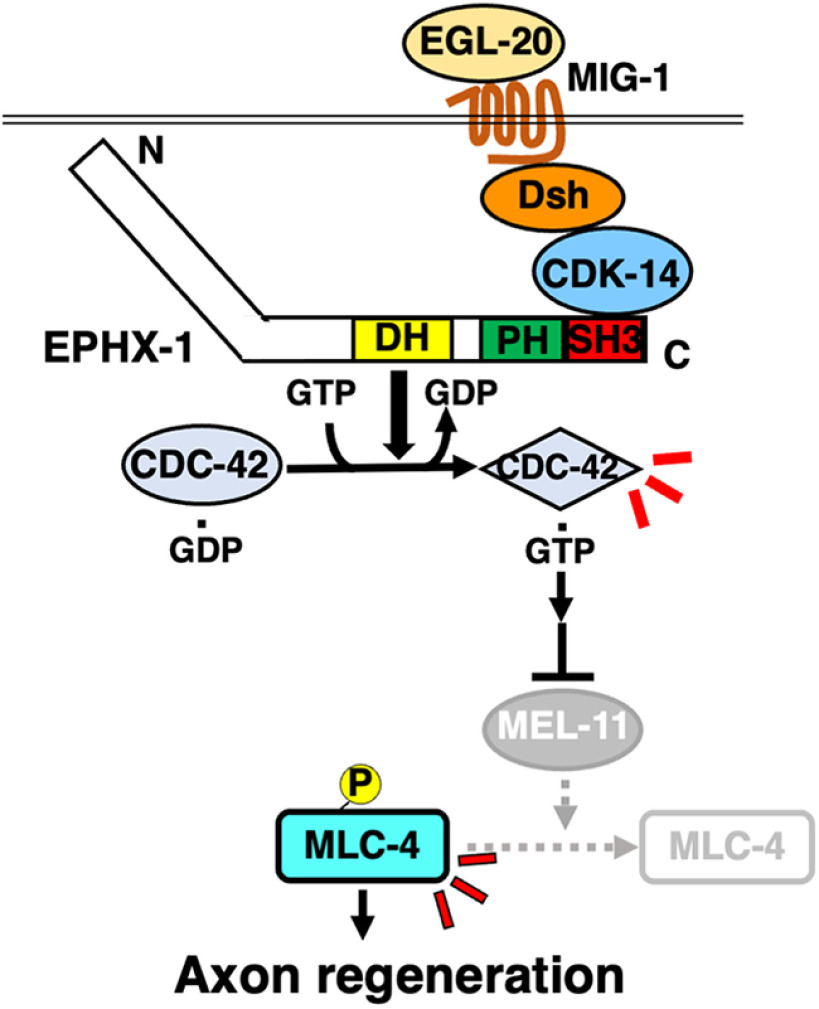
Figure 9.
Schematic model for the regulation of axon regeneration by the noncanonical Wnt signaling pathway. The EGL-20/Wnt–MIG-1/Fz signaling promotes axon regeneration by activating the noncanonical Wnt pathway consisting of the CDK-14–EPHX-1–CDC-42–MLC-4 phosphorylation axis. The exchange potential of EPHX-1 is autoinhibited by an intramolecular interaction between the SH3 domain and the N-terminal region. CDK-14 binding to the SH3 domain of EPHX-1 removes the SH3 domain from the N-terminal region, thereby activating the exchange potential of EPHX-1 toward CDC-42. Finally, GTP-bound CDC-42 causes the inactivation of MEL-11, leading to MLC-4 phosphorylation, which promotes axon regeneration.