Figure 1.
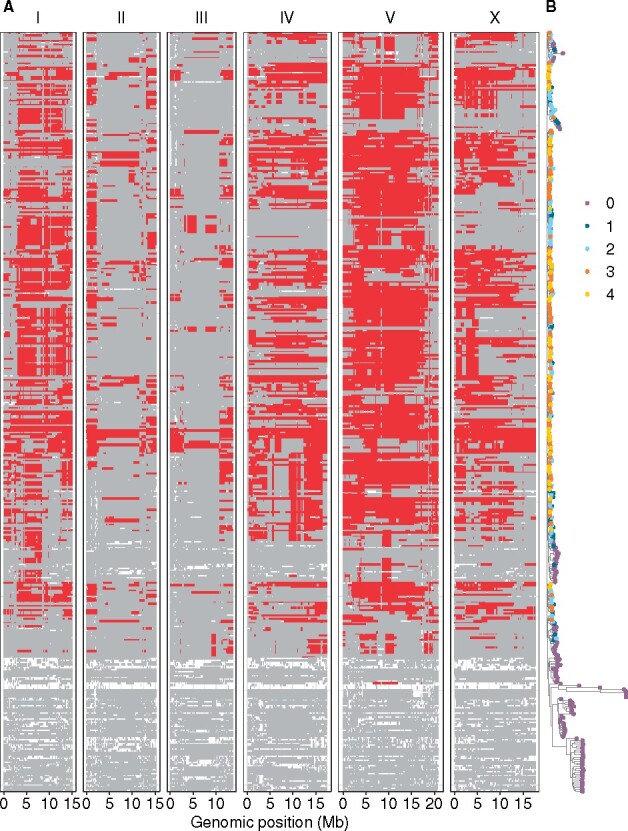
Swept chromosomes and genetic relatedness of wild C. elegans isotypes. (A) Sharing of the most common haplotypes (red) across the genome of C. elegans for 403 isotypes is shown. Genomic regions of unswept haplotypes (haplotypes other than the most common haplotypes) are colored gray. White segments are undetermined haplotypes in regions where no identical-by-descent groups were found (Crombie et al. 2019). The genomic position is plotted on the x-axis. Each row on the y-axis represents one of the 403 isotypes, ordered as their positions in (B). (B) A tree showing genetic relatedness of the 403 C. elegans isotypes, using 1,074,596 biallelic segregating sites, is shown. The tips of the tree are colored by the number of swept chromosomes (purple for zero, deep blue for one, light blue for two, orange for three, and gold for four) in each C. elegans isotype.
