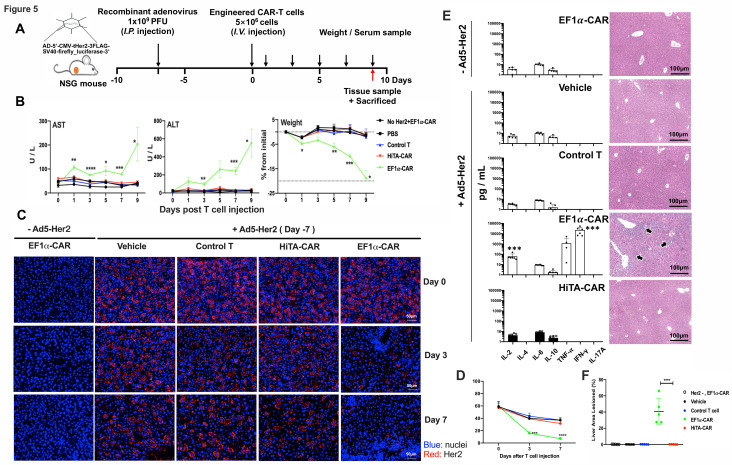
Figure 5.
HiTA-CAR-T-cells demonstrated no systemic toxicity to mice with human Her2 antigen on hepatocytes. (A) Overview of the experimental design for evaluating safety of HiTA-CAR-T cells in human Her2-expressing mice. All mice (except mice in Her2-, EF1α-CAR group) were injected (i.p.) with 1×109 PFU Ad5-Her2 and received 5×106 transduced (GPF+) T cells (intravenous) at day 8. Mice that had hepatic Her2 expression (+Ad5-Her2) but infused with vehicle, control T cells (untransduced T cells), or mice that received EF1α-CAR-T cells but lacked hepatic Her2 expression (- Ad5-Her2) served as negative control. Mice that had hepatic Her2 expression but infused with EF1α-CAR T cells served as positive control. (B) Liver damage was determined by serum ALT and AST levels collected at indicated time points. Weight change shown by percent change from initial weight (n=5–8, mean±SD is shown, a one-way ANOVA test was performed, and comparisons are shown between the HiTA-CAR and EF1α-CAR groups, *p<0.5, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (C) Detection of the kinetic expression of Her2 in hepatocytes. Her2 expression was monitored by anti-Her2 immunofluorescence staining of paraffin-embedded liver section slides at day 0/3/7 post T cells transfer separately. (D) The statistical results of Her2 +hepatocytes in different groups (n=3, mean±SD is shown, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, analyzed using Student’s t-test). (E) Systemic cytokine release by T cells 7 days post T cells transfer was detected in mouse serum by CBA assay (left) (n=5–8, mean±SD is shown, a one-way ANOVA test was performed, and comparisons are shown between the HiTA-CAR and EF1α-CAR groups, ***p<0.001). Representative hepatic tissue slides by HE staining. Black arrows indicate inflammatory lesions (right). (F) The statistical results of liver inflammatory lesioned proportion of mice in different groups (n=5, mean±SD is shown, ****p<0.0001, analyzed using Student’s t-test). ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ANOVA, analysis of variance; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; EF1α, eukaryotic elongation factor 1-α; HiTA, hypoxia-inducible transcription amplification; i.p., intraperitoneally; i.v., intravenous; CBA, cytometric bead array.