Figure 5.
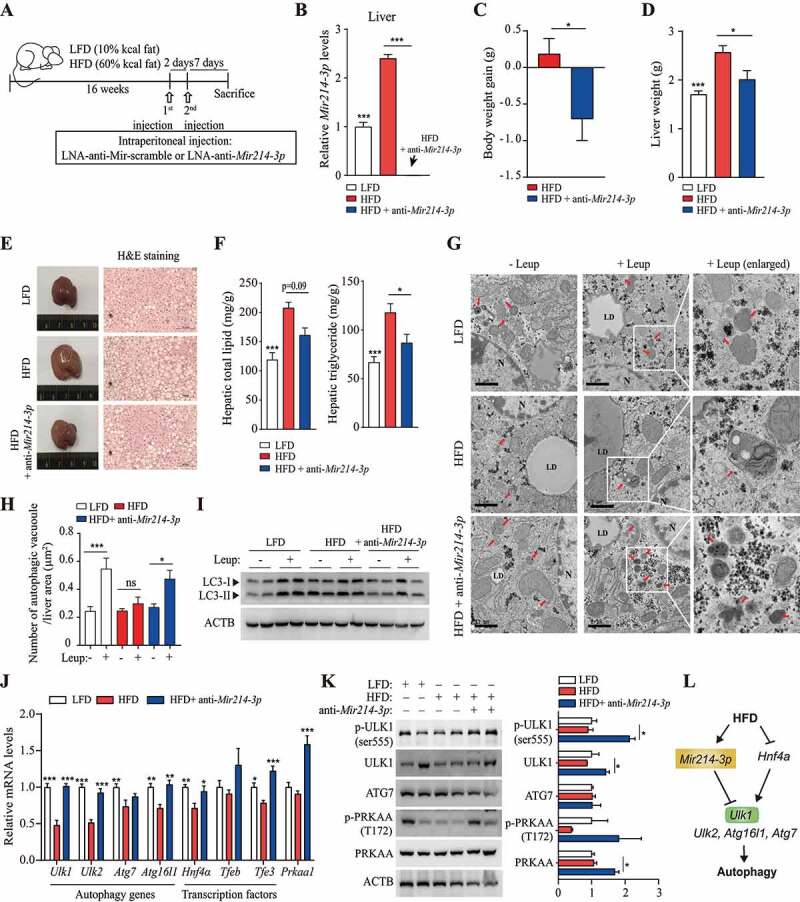
Inhibition of Mir214-3p ameliorated hepatic steatosis in HFD-fed mice. (A) nonalcoholic fatty liver was induced by 60 kcal% HFD feeding for 16 weeks and LNA-anti-Mir214-3p was administered twice intraperitoneally to inhibit Mir214-3p levels. (B) Mir214-3p levels in the liver were measured 1 week after the final LNA-anti-Mir214-3p administration. (C) Final body weight gain. (D) Liver weight. (E) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the liver. (F) Hepatic total lipid and triglyceride levels were measured in the liver. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 10). * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001, compared to the HFD-fed group. (G) Representative TEM images of autophagic vacuoles in the liver. In the enlarged insets, autophagosome aggregation is observed in Leup-treated livers. Scale bar: 1 μm (H) The number of autophagic vacuoles per μm2 of liver area was quantified. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 10). * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001, compared to the group not treated with Leup. (I) The LC3 protein levels in the liver in the presence or absence of Leup. (J) The expression of Mir214-3p target genes was measured using qRT-PCR. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 6). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, compared to the HFD group. (K) Liver tissue levels of proteins encoded by genes targeted by Mir214-3p. (L) Schematic overview of this study. Mir214-3p directly downregulates Ulk1 expression to ultimately inhibit autophagic activity. Reduced expression of Hnf4a by HFD feeding also reduced Ulk1 expression, leading to hepatic steatosis. PRKAA/AMPKa: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, alpha catalytic subunit; HFD: high-fat diet; Leup: leupeptin; LFD: low-fat diet; LNA: locked nucleic acid; qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; SEM: standard error of mean; TEM: transmission electron microscopy
