Figure 6.
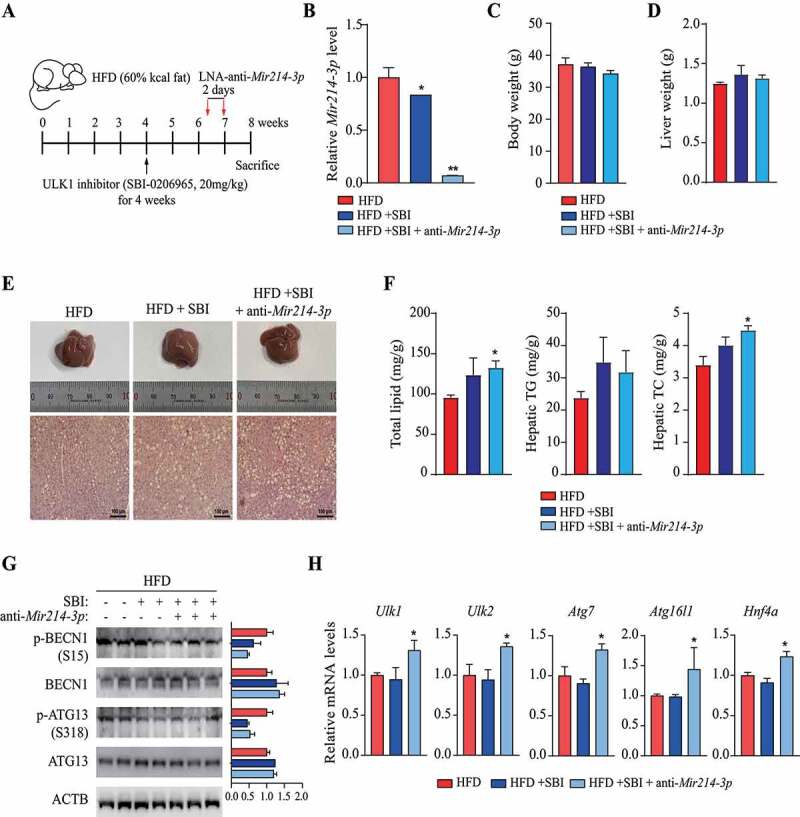
Regulation of Ulk1 expression by Mir214-3p is important for the mitigation of hepatic steatosis. (A) Scheme of in vivo experiments. To induce nonalcoholic fatty liver, mice were fed 60 kcal% HFD. At 4 weeks, SBI-0206965 (ULK1 inhibitor) was injected intraperitoneally to reduce ULK1 activity, and LNA-anti-Mir214-3p was administered twice after 2 weeks. (B) Relative Mir214-3p levels in the liver tissue. These levels were measured 1 week after the final anti-Mir214-3p administration. (C) Final body weight. (D) Liver weight. (E) Representative images of H&E-stained liver section. Scale bar: 100 μm (F) Total hepatic lipid, triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) levels. (G) Protein production from autophagy-related genes in the liver. Levels of proteins phosphorylated by ULK1 to induce autophagy were measured in the liver. (H) mRNA levels of autophagy genes targeted by Mir214-3p. Values represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. BECN1: beclin 1; H&E: hematoxylin and eosin; HFD: high-fat diet; LNA: locked nucleic acid; SEM: standard error of mean
