Figure 2.
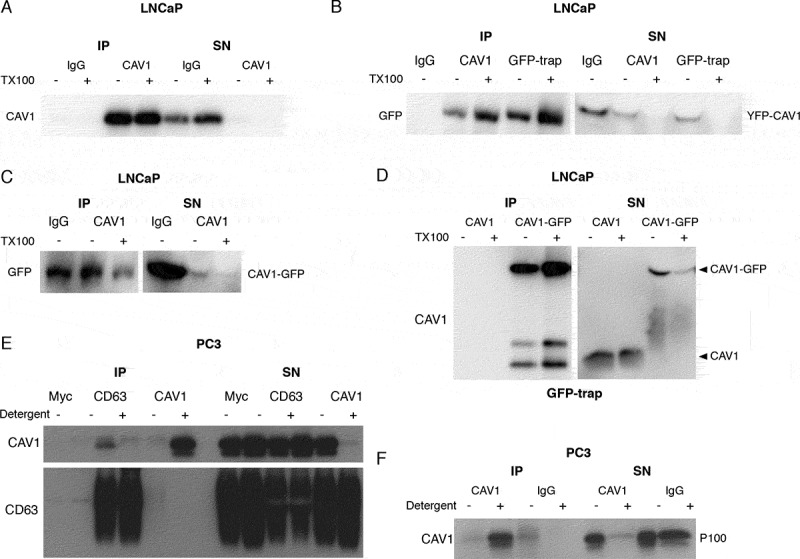
LNCaP cells release CAV1 in an antibody-accessible form. (A) Western blot of an immunoprecipitation of CAV1 from the S100 fraction of LNCaP cells with 48-h serum starvation with an α-CAV1 antibody demonstrating CAV1 can be immunoisolated in the absence of detergent. (B-D) CAV1 in the S100 fraction from LNCaP cells with 24-h serum starvation can be pulled down by anti-CAV1 antibodies and GFP-trap binding to fusion tags at both the N- and C-termini of CAV1 without detergent treatment. No tagged CAV1 was used as a negative control for GFP-trap in Figure 2D. (E) Immunoprecipitation of culture medium from 16-h serum-starved PC3 cells with an α-CD63 antibody results in the pulldown of CAV1 in the absence of detergent whereas immunoprecipitation with an anti-CAV1 antibody does not result in the isolation of CAV1 unless pre-treated with a detergent. (F) Western blot demonstrating pulldown of CAV1 from the P100 fraction of PC3 cells with 16-h serum starvation is dependent on detergent treatment. All western blots are representative blots chosen from three independent replicates
