Figure 6.
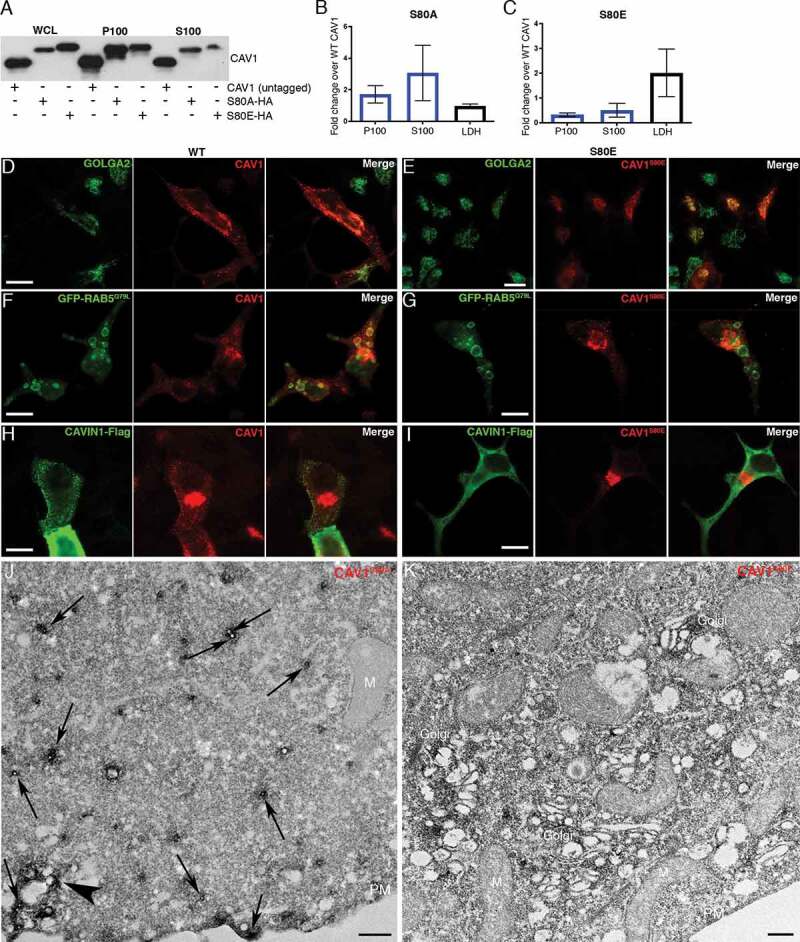
CAV1 mutants are differentially released from LNCaP cells. (A) Western blot of the S100 and P100 fractions of CAV1 released from S80A and S80E expressing LNCaP cells with 16-h serum starvation. (B) A relative increase in the release of the S80A in both the P100 and S100 fractions was observed compared to WT (n = 3). (C) A relative reduction in the release of the S80E mutant was observed compared to WT. While LDH levels were increased with the expression of the CAV1S80E mutant, this would likely result in a corresponding increase in the nonspecific release of. Despite this, a two-fold reduction in secreted CAV1 levels were observed. (D) WT CAV1 partially co-localizes with GOLGA2 at the Golgi complex, scale bar: 10 τm. (E) The S80E mutant is almost exclusively localized to the Golgi complex, scale bar: 20 τm. (F) WT CAV1 is sorted into GFP-RAB5Q79L positive compartments, scale bar: 10 τm. (G) S80E mutant is not efficiently sorted into GFP-RAB5Q79L-positive endosomes, scale bar: 10 τm. (H) CAVIN1-Flag expression stabilizes CAV1 in punctate structures at the PM of LNCaP cells, scale bar: 10 τm. (I) CAVIN1-Flag expression does not stabilize CAV1 at the surface of LNCaP cells and CAVIN1 remains cytoplasmic/soluble when co-transfected with the S80E mutant, scale bar: 10 τm. (J) LNCaP cells demonstrating the S80A point mutant efficiently generated C-exosome precursors in the cytoplasm. C-exosomes = black arrows. Scale bar: 500 nm. (K) LNCaP cells expressing YFP-CAV1S80E mutant construct. The point mutation predominantly is localized to the Golgi complex and is inefficient in generating small CAV1-rich vesicles. Scale bar: 500 nm. Fluorescent images are representative images from three independent replicates. Electron micrographs are representative images; each LNCaP experiment was independently replicated three times
