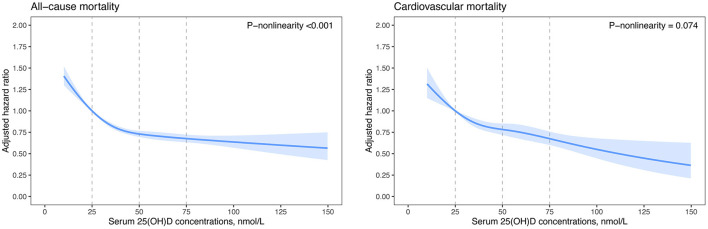
Figure 1.
Dose-response curves for serum 25(OH)D concentrations and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Hazard ratios (blue lines) and 95% confidence intervals (light blue shade) were adjusted for age (continuous), sex (male, female), and ethnicity (White, mixed, Asian, Black, Chinese, others, or unknown), education (college or university, vocational qualification, upper secondary, lower secondary, others, or unknown), Townsend deprivation index (in quintiles), household income (<18,000, 18,000–30,999, 31,000–51,999, 52,000–1,00,000, >1,00,000 £, or unknown), smoking status (never smoker, former smoker, current smoker, or unknown), alcohol consumption (0, 0.1–4.9, 5.0–14.9, 15.0–19.9, 20.0–29.9, ≥30.0 g/day, or unknown), physical activity (inactive group, insufficient group, active group, or unknown), healthy diet score (in quintiles), and BMI (<18.5, 18.5–22.9, 23.0–24.9, 25.0–29.9, 30.0–34.9, or ≥35.0 kg/m2), eGFRcr-cys (<30.0, 30.0–60.0, 60.0–90.0, ≥90.0 ml min−1 per 1.73 m2), C-reactive protein (in quintiles), antihypertensive medication use (yes, no), cholesterol lowering medication use (yes, no), diabetes medication use (none, only oral medication, only insulin, or insulin and oral medication), history of cancer, diabetes, hypertension, and duration of CVD (<1.0, 1.0–4.9, 5.0–9.9, or ≥10.0 years). BMI, body mass index; CVD, cardiovascular disease; eGFRcr-cys, estimated glomerular filtration rate (creatinine–cystatin C equation).