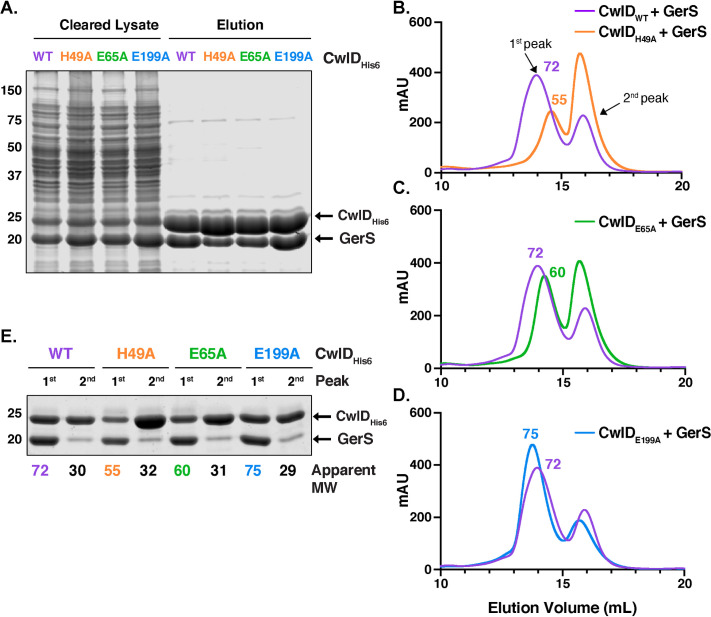
Fig 3. Mutation of CwlD Zn2+-binding residues, His49 and Glu65, decreases the stability of the CwlD:GerS complex.
(A) Coomassie stain of wild-type CwlD-His6, H49A, E65A or E199A His-tagged CwlD variants co-affinity purified with untagged GerS. The indicated proteins were produced in E. coli and purified using Ni2+- affinity resin. Cleared lysate and eluate fractions were analyzed using Coomassie staining. Comparison of the size exclusion chromatography traces of the wild-type CwlD:GerS complex with CwlDH49A:GerS (B), CwlDE65A:GerS (C) and CwlDE199A:GerS (D) complexes. mAU corresponds to the UV absorbance measurements (A280) during the protein elution. The 1st peak of each trace corresponds to the protein complex; the estimated molecular weight (MW) in kDa of the complex is given on top of this first peak. (E) Coomassie stain of fractions corresponding to the 1st and 2nd peak of each trace. The numbers at the bottom correspond to the apparent MW of each peak. The data shown are from one biological replicate, which is representative of three biological replicates performed independently.