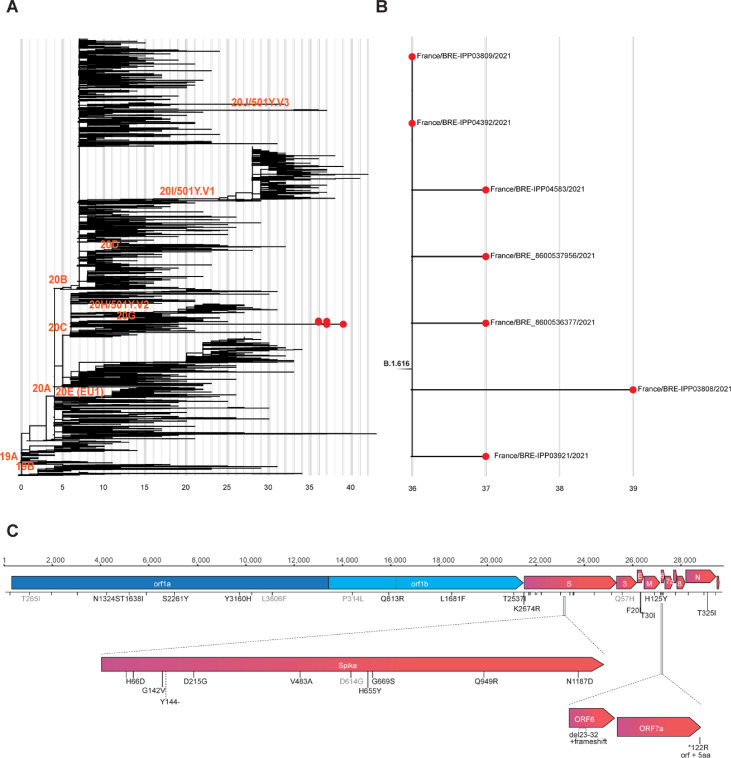
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the B.1.616 lineage of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and characteristic non-synonymous substitutions. (A) Subsampled global phylogenetic maximum likelihood tree of SARS-CoV-2 with annotated Nextstrain clades next to the corresponding nodes and tips highlighted only for sequences from the Pangolin B.1.616 lineage. (B) Detailed view of the B1.616 lineage. In (A) and (B) branch lengths correspond to the number of nucleotide substitutions (shown below the tree) from the reference Wuhan-Hu-1 strain (NC_045512). (C) Nucleotide and amino-acid substitutions from the reference Wuhan-Hu-1 strain shared among the sequences from Lannion, France are represented as ticks along the SARS-CoV-2 genome and are annotated with text if non-synonymous. Light grey text annotated amino-acid substitutions are not unique to the Lannion (B1.616) lineage.