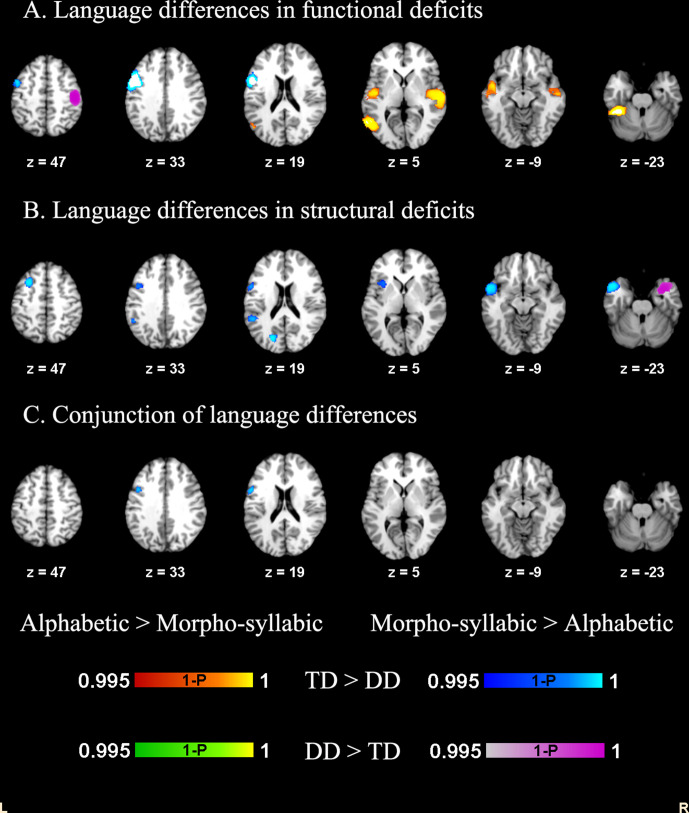
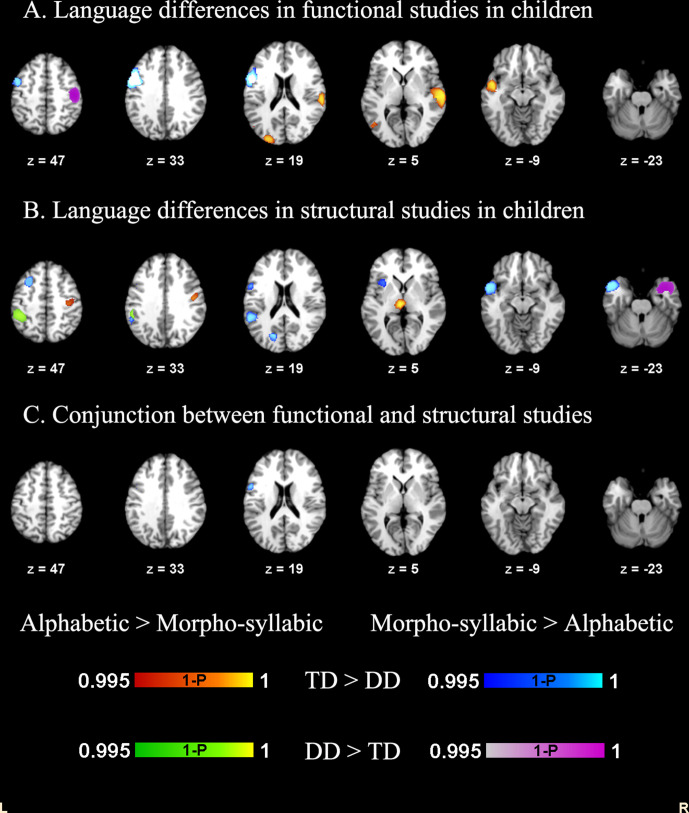
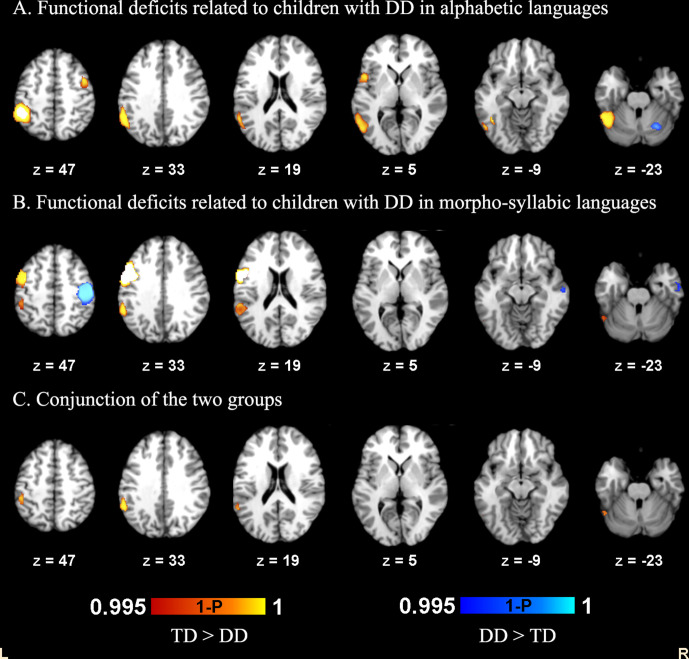
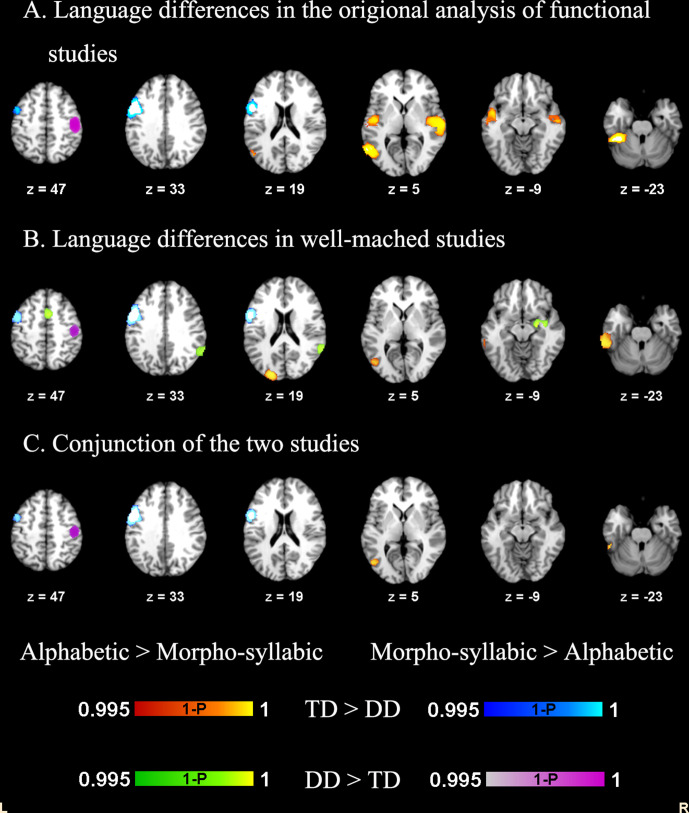
Figure 2. Direct comparisons between the alphabetic group and the morpho-syllabic group in structural and functional deficits.
Conjunction analysis showed greater reduction of both GMV and brain activation in the left dorsal IFG in morpho-syllabic languages than alphabetic languages.