Fig. 2.
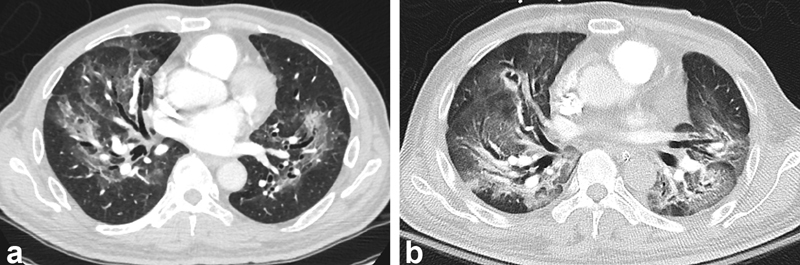
Radiation pneumonitis complicating radioembolization. A 56-year-old man with chronic hepatitis B and unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in the right hepatic lobe with portal vein and inferior vena cava invasion was treated with hepatic radioembolization. Mapping angiography was completed, and the lung shunt fraction was estimated at 22%. He was treated with an estimated dose of 27 Gy. The patient developed dyspnea, and CT chest 4 months after treatment showed changes of “batwing” appearance of ground-glass attenuation with peripheral sparing ( a ). Despite treatment with steroids, symptoms were progressive on CT findings ( b ). The patient died shortly thereafter.
