Figure 1.
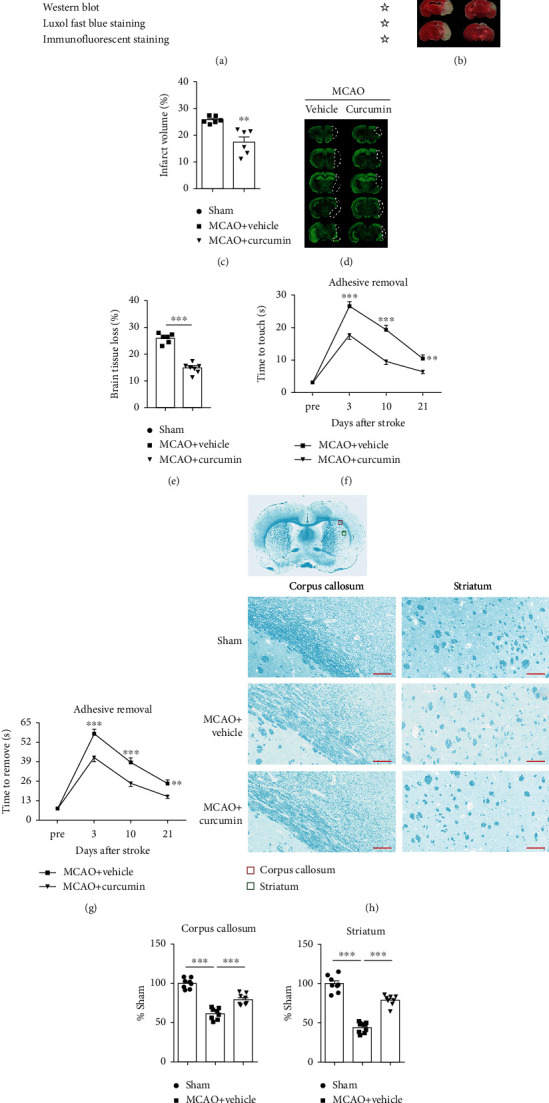
Curcumin treatment significantly reduces white matter injury and improves sensorimotor function after ischemic stroke. Mice were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and then treated with curcumin (150 mg/kg, i.p.) immediately after reperfusion and once daily for 7 days after ischemia. (a) Illustration of the in vivo experimental timelines. (b) Representative TTC staining and (c) quantification of the infarct volume at 3 days after MCAO. n = 6 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01. Student's t-test. (d) Representative MAP-2 staining and (e) quantification of brain tissue loss at 21 days after MCAO. n = 6 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01. Student's t-test. (f, g) Adhesive removal was used to evaluate long-term sensorimotor deficits at pre-MCAO and 3, 10, and 21 days after surgery. (f) Time to touch adhesive tapes; (g) time to remove adhesive tapes, n = 8 for each group. Data are presented as means ± SEM. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. (h) Schematic diagram illustrating the anatomical location of images in the ipsilateral perilesion corpus callosum (red) and striatum (green). Representative Luxol fast blue (LFB) staining in the ipsilateral peri-infarct corpus callosum (CC) and striatum areas 21 days after MCAO. Scale bar = 50 μm. n = 8 for each group. (i, j) The integrated density of LFB staining was quantified and normalized to the sham group. ∗∗p < 0.05 vs. vehicle. One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
