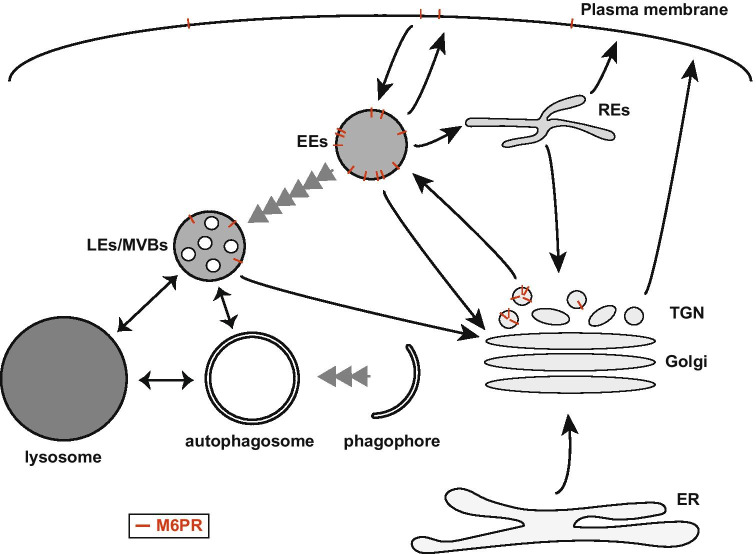
Fig. 1.
Simplified overview of the secretory and endolysosomal systems, and the principal glycoprotein transport routes. The synthesis of signal-peptide marked soluble and transmembrane (glyco)proteins on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) leads to their translocation into the ER lumen or membrane, respectively. While some of the nascent proteins possess retention signals to let them remain localized in this compartment, others are transported to their final destination through sorting mechanisms that rely on the presence and/or absence of targeting signals that are encoded in peptide motifs and glycans. Integral plasma membrane and secreted (glyco)proteins reach the cell surface by vesicular traffic, passing through the Golgi. Endocytosed (imported) (glyco)proteins are delivered to the early endosomes (EEs), which are also the principal arrival point for newly synthesized (glyco)proteins destined to the endolysosomal system, sorted out from the secretory pathway at the trans-Golgi network (TGN). EEs are an important hub for (glyco)protein sorting and distribution. Lysosomal protein-sorting receptors can be recycled from EEs back to the Golgi for re-use, while plasma membrane proteins can be trafficked to the plasma membrane directly or via recycling endosomes (REs). Lysosomal soluble and transmembrane (glyco)proteins, however, remain associated with the EEs, and reach lysosomes through the maturation of EEs into late endosomes/multivesicular bodies (LEs/MVBs), which are characterized by the formation of intraluminal vesicles. LEs/MVBs finally fuse with lysosomes to deliver their membrane-associated and luminal cargos to this organelle. Autophagosomes arise through the generation and expansion of a phagophore, and when complete, they fuse either first with LEs and then lysosomes or directly with lysosomes. Arrows indicate the direction of main transport routes. Double-head arrows highlight fusion events between organelles. Serial arrowheads designate maturation processes. The Man-6-phosphate receptors (M6PRs, red bars) are highlighted in the compartments through which they are trafficking. M6PRs are mostly present in the TGN and EEs, but they can also be detected at the plasma membranes and LEs/MVBs