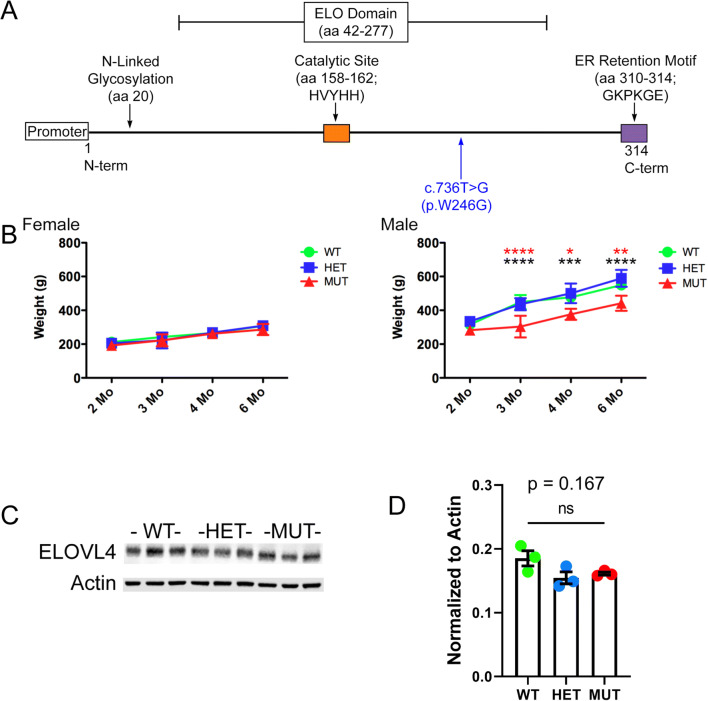
Fig. 1.
Knock-in of the W246G ELOVL4 mutation, physical differences, and ELOVL4 expression in WT, HET, and MUT rats. A Cartoon depicting the overall structure and functional domains of ELOVL4 and the location of the W246G ELOVL4 mutation. B The W246G ELOVL4 mutation does not affect the size of female rats at any age between 2 months and 6 months of age. Male MUT rats are significantly smaller than age-matched WT and HET rats from 3 months of age (females, 2 months: n = 26 WT, 22 HET, 24 MUT; 3 months: n = 17 WT, 13 HET, 17 MUT; 4 months: n = 9 WT, 9 HET, 10 MUT; 6 months: n = 17 WT, 14 HET, 10 MUT. Males, 2 months: n = 5 WT, 8 HET, 4 MUT; 3 months: n = 5 WT, 8 HET, 4 MUT; 4 months: n = 4 WT, 7 HET, 3 MUT; 6 months: n = 7 WT, 10 HET, 4 MUT. Data are shown as mean ± SD. 1-way ANOVA + Bonferroni post-hoc test. *p< 0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001). C Western blot of cerebellum from WT, HET, and MUT rats (n=3 each). D Quantification of ELOVL4 levels (normalized to Actin loading control) showed no differences across genotypes. Analysis performed on samples from 3 different rats of each genotype (data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test)