Figure 2.
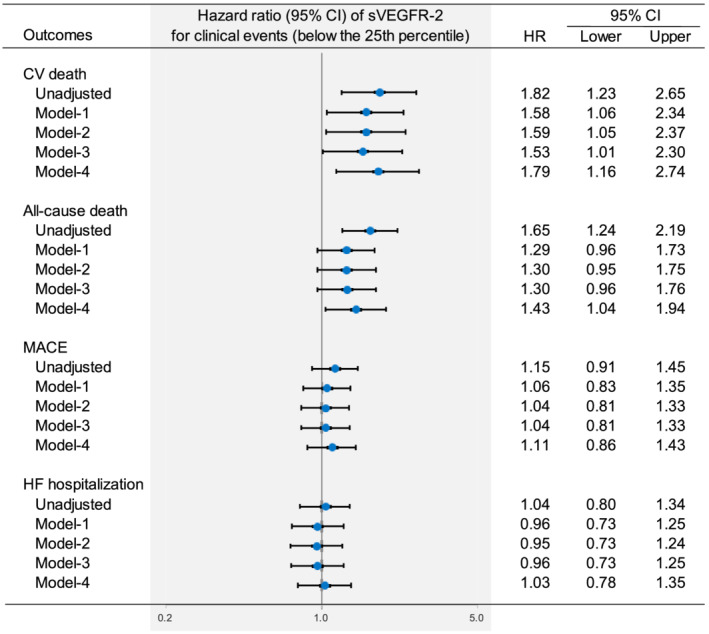
Multivariate Cox proportional hazard analysis for CV death, all‐cause death, MACE, and HF‐related hospitalization. Model 1: adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, and traditional cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidaemia), as well as established risk factors for HF [prior HF hospitalization, left ventricular dysfunction (ejection fraction < 40%), and NYHA class 3/4]. Model 2: adjusted for the covariates included in Model 1 and other CV risk factors (CAD, old myocardial infarction, AF, CKD, anaemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and cerebrovascular disease). Model 3: adjusted for the covariates included in Model 2 and prescription of RAS‐I, beta blockers, loop diuretics, and MRA. Model 4: adjusted for the covariates included in Model 3 and CV biomarkers [NT‐proBNP, hs‐cTnI, and hs‐CRP (>1 mg/L)]. AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CAD, coronary artery disease; CKD, chronic kidney disease; hs‐CRP, high sensitivity C‐reactive protein; hs‐cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; MRA, mineral corticoid receptor antagonists; NT‐proBNP, N‐terminal pro‐brain natriuretic peptide; RAS‐I, renin angiotensin inhibitor. Other abbreviations are defined in Figure 1 .
