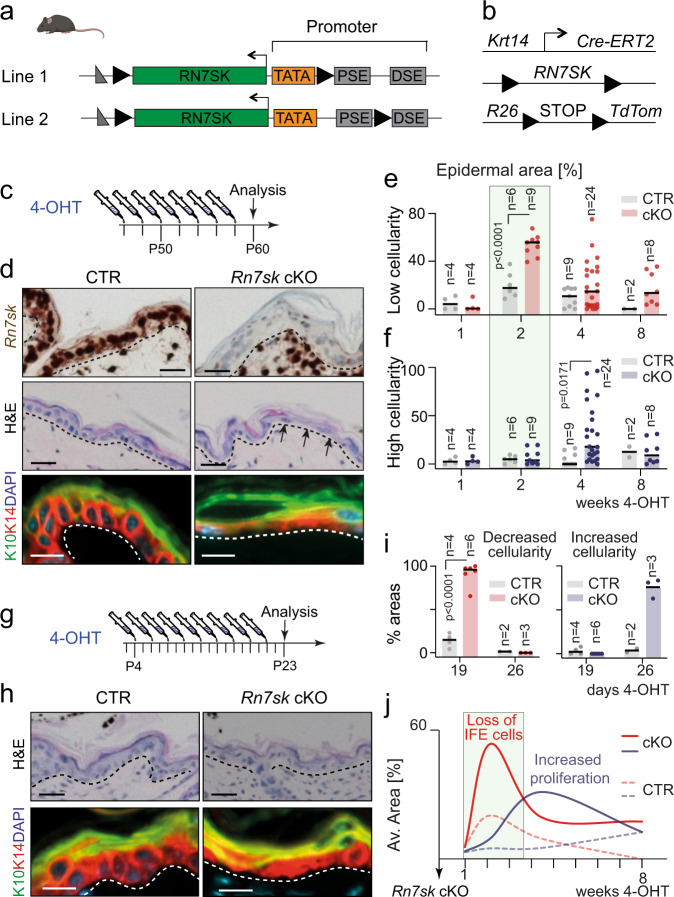
Fig. 1. Rn7sk regulates cellularity in the mouse epidermis.
a Schematic representation of the targeted Rn7sk alleles in the two mouse lines generated. loxP sites = black triangles; TATA = TATA box; PSE = proximal sequence elements; DSE = distal sequence elements. b Schematic representation of the transgenes used to delete Rn7sk within the interfollicular epidermis (IFE). c Treatment regime of the experiment shown in (d). d Rn7sk RNA in situ hybridization (brown; top panel), haematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E, middle panel) and KRT10 (K10; green) and KRT14 (K14; red) immunofluorescence (bottom panel) of control (CTR) and Rn7sk knock-out (Rn7sk cKO) mice. e, f Quantification of skin area with reduced (red) (e) or increased (blue) (f) epidermal cellularity at the indicated time points (n = mice). g Treatment regime of the experiment shown in (h, i). h H&E staining (top panel) and KRT10 (K10; green) and KRT14 (K14; red) immunofluorescence (bottom panel) of mice treated with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) as shown in (g). DAPI (blue): nuclear counterstain (d, h). i Quantification of skin area with decreased (red; left panel) or increased (blue; right panel) epidermal cellularity in mice treated as shown in (g) (n = mice). J Graphical summary of the data shown in (e, f, i). Mouse line 1 was used in (d, h, i). Pooled data from mouse lines 1 and 2 are shown in (e, f). Scale bar: 10 μm (d, h). Shown is mean. Multiple two-tailed unpaired t-tests. Exact p-values are indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.