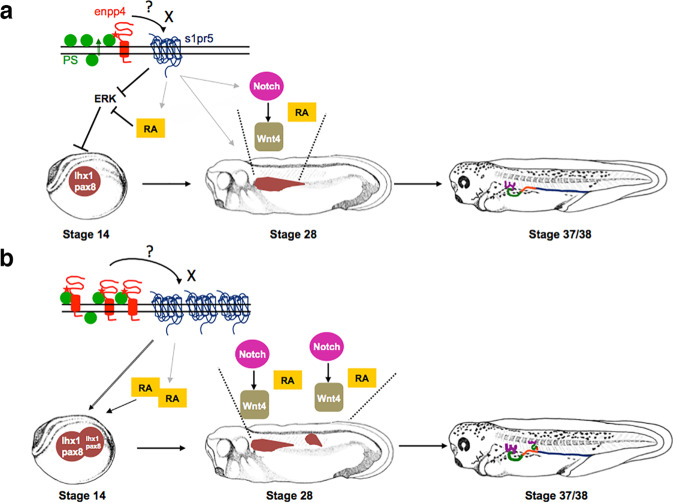
Fig. 8. Proposed model of how Enpp4/S1pr5 controls pronephros patterning.
a During normal pronephric development, in the extracellular space, Enpp4 binds to phosphatidylserine close to, or in its catalytic site, which can then either interact with the S1pr5 or produce a novel ligand X, able to bind to this receptor. The activation of S1pr5 leads to the upregulation of lhx1/pax8 pronephric markers in the kidney field either by acting upstream of RA signalling pathway or by acting directly via the ERK or calcium pathways. At later stages, RA is required for tubules morphogenesis and Notch and Wnt pathway are involved in the patterning of the pronephric tubules. The mechanism by which S1pr5 activation directs the expression domains of these genes remains to be confirmed. b Enpp4 and S1pr5 overexpression lead to expanded and ectopic expression domains for both the Notch and RA pathway genes and wnt4. These changes in patterning gene expression domains induce the formation of enlarged pronephric segments and ectopic pronephric tubules.