Figure 3.
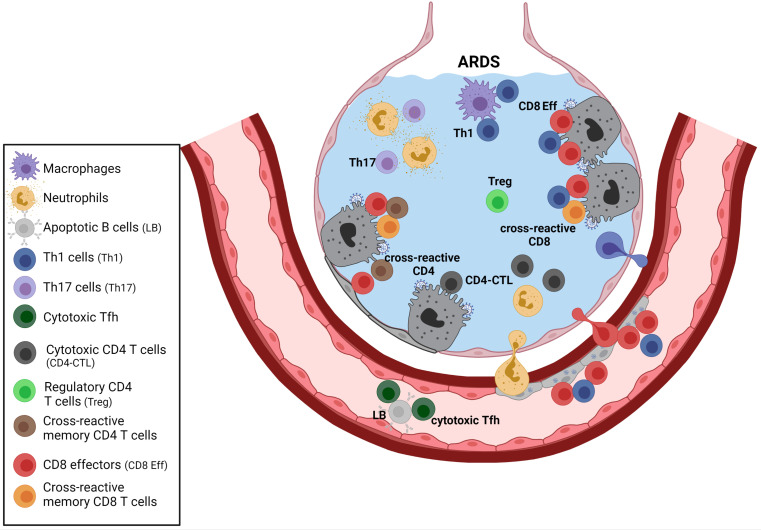
T cell responses during severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. The complex network of CD4 T cell responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection involves different CD4 subsets, including Treg, Th1 cells, Th17 cells, and some cytotoxic CD4 subsets. Th17 cells may activate neutrophils, and Th1 may provide helping signals to macrophages and CD8 effectors. Cytotoxic CD4 T cells that produce multiple chemokines (that may recruit myeloid cells) and direct cytotoxic properties have been reported in patients with severe disease. Those cytotoxic CD4 subsets could exert cytotoxicity on infected type II pneumocytes that can express MHC class II. The role of cross-reactive memory CD4 T cells generated following previous infections with endemic coronaviruses remains to be clarified. Those activated cross-reactive cells may provide help to various immune effectors, including SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8 primary effectors or coronavirus cross-reactive CD8 memory T cells (secondary effectors). Circulating cytotoxic Tfh that may kill B cells have also been described. The diminution of Treg reported in severe ARDS may exacerbate T cell mediated immunopathology. Created with BioRender.com.