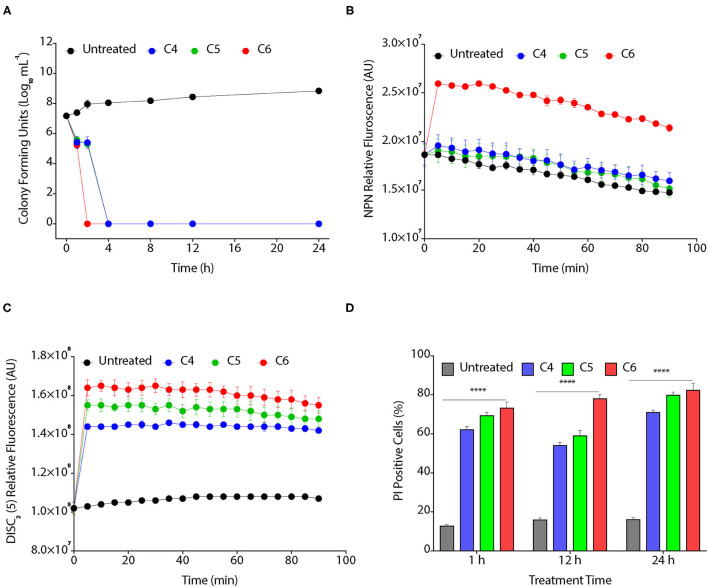
Figure 2.
CAGCs affect bacterial membranes. (A) Time kill assay on the treatment of Xoo with 8 μg/ml of C4, C5, and C6 CAGCs. (B) Time-dependent change in fluorescence of N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine (NPN) in presence of different CAGCs. (C) Change in fluorescence intensity of 3, 3′-diethylthiadicarbocyanine iodide (DiSC2) (5) over time after treatment of Xoo with different CAGCs. (D) Percentage of PI positive Xoo cells at a different time on treatment of Xoo with 8 μg of different CAGCs. The NPN and DISC2(5) fluorescence were measured at λex of 350 nm, λem of 420 nm, and λex of 637 nm, λem of 670 nm by spectrophotometry. The number of Xoo live cells with response to CAGCs were measured using FACS. Error bars indicate that experiments were repeated a minimum of three times with four biological replicates. (α = 0.05, ****p < 0.0028). Significant differences were determined by using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD analysis.