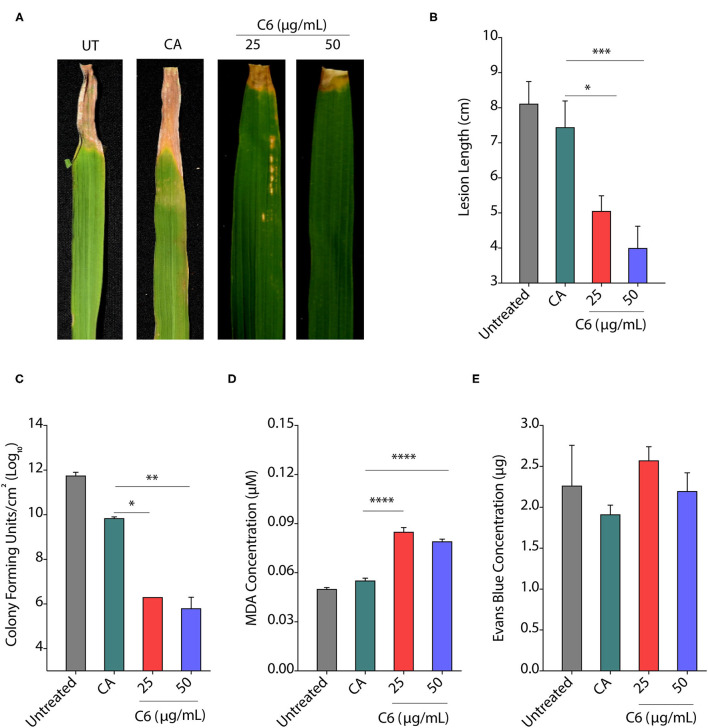
Figure 6.
Seed priming provides protection from infection. (A, B) Pictures showing the bacterial disease symptoms at 15 dpi (A) and change in lesion length at 30 dpi (B) after priming of rice seedlings with C6 CAGC. (C–E) Change in CFUs (C), lipid peroxidation derived malondialdehyde (MDA) levels (D), and membrane stability assessment by Evan's blue dye quantification (E) of infected leaves at 5 dpi after priming with C6 at 25 and 50 μg/ml. For priming, rice seeds were soaked in C6 at 25 and 50 μg/ml overnight followed by vacuum infiltration for 5 min, and seedlings were established in the soil. About 30 day-old plants were infected with Xoo (106 cfu/ml). The experiment was repeated three times with minimum of 10 biological replicates. Values are means + SE from three biological replicates. A significant difference was determined by using two-way ANOVA with Tukey's HSD test (α = 0.05, * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).