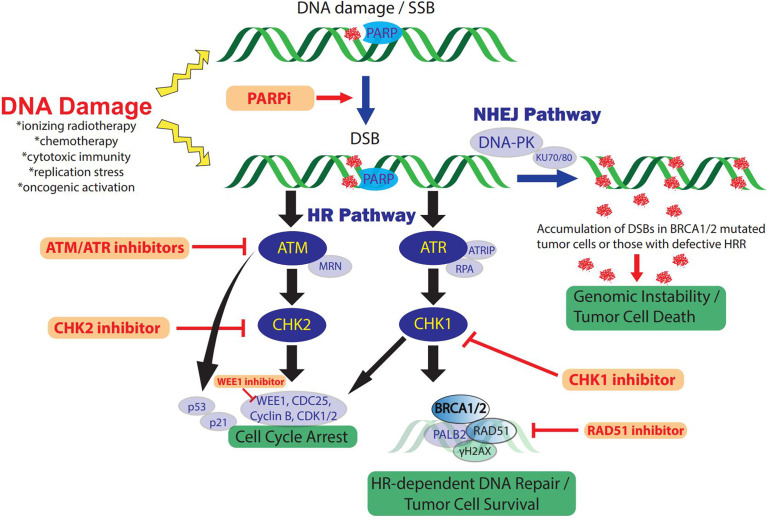
Figure 1.
The DDR and therapeutic strategies in TNBC. DNA-damaging therapies or endogenous replication dysfunction result in SSBs and DSBs which activate the DDR and repair signaling pathways. Distinct DSB DDR signaling pathway initiation depends on the type of DNA damage and is mediated by three central DDR kinases: DNA-PK, ATM, and ATR. In addition, PARP enzymes play a key role in DDR and facilitate SSB repair efficiency and functions in DSB repair via HRR and NHEJ pathways. The ATM and ATR pathways cross-talk extensively and only key intersections are highlighted here for pragmatic purposes. ATM/CHK2 signaling induces cell cycle arrest, preventing cell cycle progression in tumor cells with DNA damage. In addition, ATR/CHK1/WEE1 signaling initiates DNA DSB repair by inducing checkpoints and activating key components of HRR, including BRCA1/2 activity. Alternatively, DSB repair occurs through NHEJ via DNA-PKcs recruitment. Inhibition of PARP to treat TNBC with defects in HRR such as BRCA1/2 mutations, induces DSBs from unrepaired SSBs via PARP trapping and collapsed replication forks. Accumulated PARPi-induced DNA damage cannot be effectively repaired due to the HRR deficiency, resulting in genomic instability and cell cycle arrest. In addition, loss of function or inhibitors (red) against other key mediators of HRR also constrain NHEJ dependence which can be overwhelmed in the setting of concomitant PARPi via accumulation of DSB and genomic instability. RAD51 inhibition also suppresses HRR and sensitizes TNBC to PARPi. ATM/ATR/CHK1/WEE1 inhibition increases DSBs and impairs cell cycle arrest checkpoints and DNA damage repair, ultimately resulting in tumor cell death. DDR, DNA damage response; SSB, single-strand breaks; DSB, double-stranded breaks; DNA-PK, DNA-dependent protein kinase; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia-mutated; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein; NHEJ, non-homologous end-joining; HR(R), homologous recombination repair; PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PARPi, PARP inhibitor/inhibition; MRN complex, Mre11, Rad50, Nbs1; ATRIP, ATR-interacting protein; RPA, replication protein A.