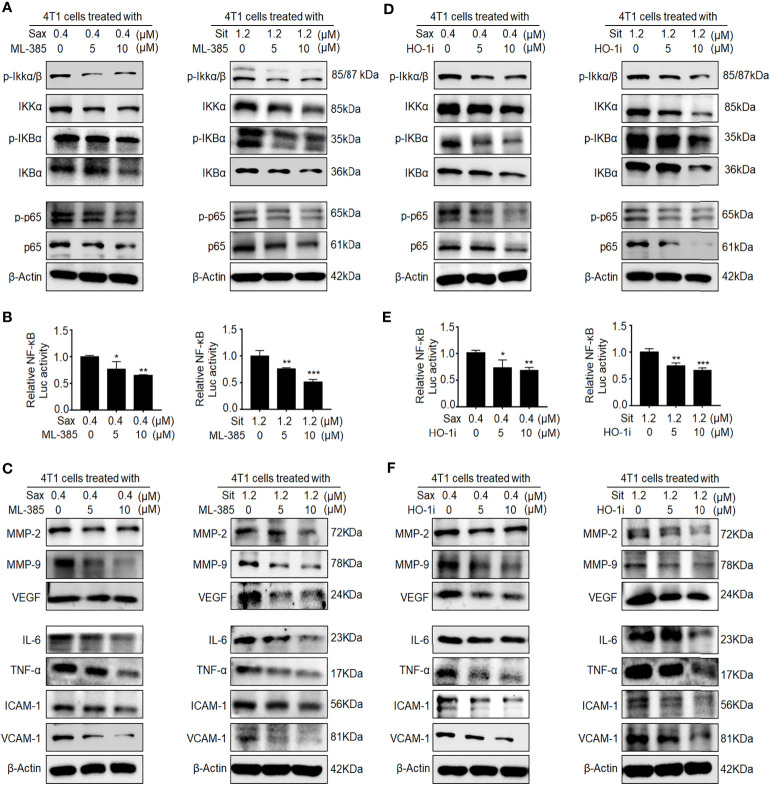
Figure 4.
Inhibition of NRF2-HO-1 activation abrogates DPP-4i-driven NF-кB activation. (A–C) NRF2 blockage abrogates DPP-4i-induced NF-кB activation. 4T1 cells were co-treated with Sax (0.4 μM) or Sit (1.2 μM) and NRF2 inhibitor ML-385 (0, 5, and 10 μM), respectively. (A) The expression of p-65, p-p65, and NF-кB regulatory proteins was detected by Western blotting. (B) NF-кB transcriptional activation was analyzed by luciferase reporter assay, and (C) NF-кB-responsive targets were detected by Western blotting. (D–F) HO-1 inhibition attenuates DPP-4i-induced NF-кB activation. 4T1 cells were co-treated with Sax (0.4 μM) or Sit (1.2 μM) and HO-1 inhibitor (0, 5, and 10 μM), respectively. (D) The expression of p-65, p-p65, and NF-кB regulatory proteins was detected by Western blotting. (E) NF-кB transcriptional activation was analyzed by luciferase reporter gene assay. (F) NF-кB-responsive targets were detected by Western blotting. β-Actin was a loading control. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Representative images are shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 between the indicated groups determined by the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).