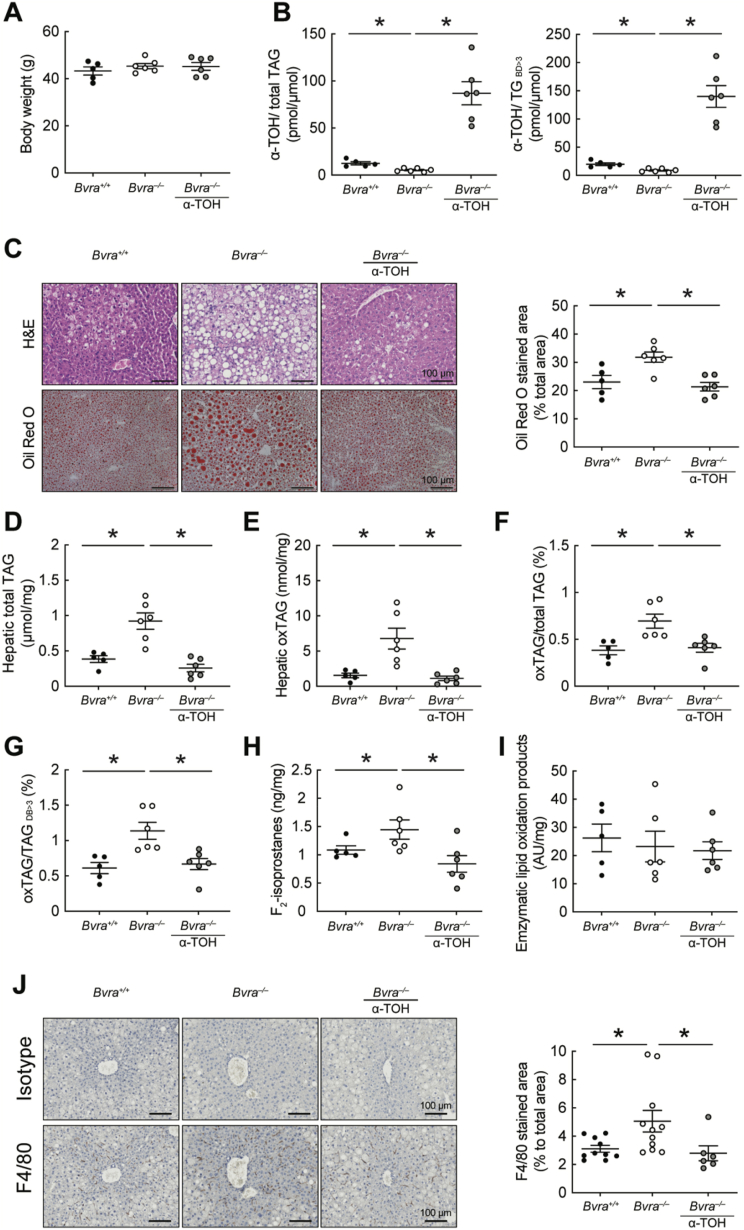
Fig. 6.
α-Tocopherol prevents hepatic lipid accumulation and lipid oxidation in Bvra–/– mice fed HF diet for 14 weeks. (A) Body weights of Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed a HF diet ± α-TOH supplement (0.2% RRR-α-TOH, w/w). (B) Ratio of hepatic α-TOH-to-TAG and α-TOH-to-TAGDB>3 in Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF diet ± α-TOH. α-TOH was measured by LC-MS/MS and results normalized to tissue weight (mg). (C) Representative H&E and Oil Red O-stained liver sections of Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF ± α-TOH. Scale bar = 100 μm, with quantification also provided. (D–G) Concentrations of hepatic total TAG, oxTAG, oxTAG-to-total TAG, and oxTAG-to-TAGDB>3 in Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF ± α-TOH. (H) Hepatic F2-IsoP in Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF diet ± α-TOH. (I) Enzymatic lipid oxidation products in the liver of Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF diet ± α-TOH. TAG and oxTAG were measured by untargeted lipidomic analysis using LC-MS/MS, F2-IsoP were measured by GC-MS and enzymatic lipid oxidation products by ion mobility Q-TOF LC/MS. (J) IHC of F4/80 and rat IgG isotype control in liver sections of Bvra+/+ and Bvra–/– mice fed HF diet ± α-TOH, with corresponding quantitative data of F4/80 positive area. Scale bar = 100 μm. Numerical results show individual data as well as mean ± SEM, with data analyzed for statistical difference using the Kruskal Wallis test. *P < 0.05. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)