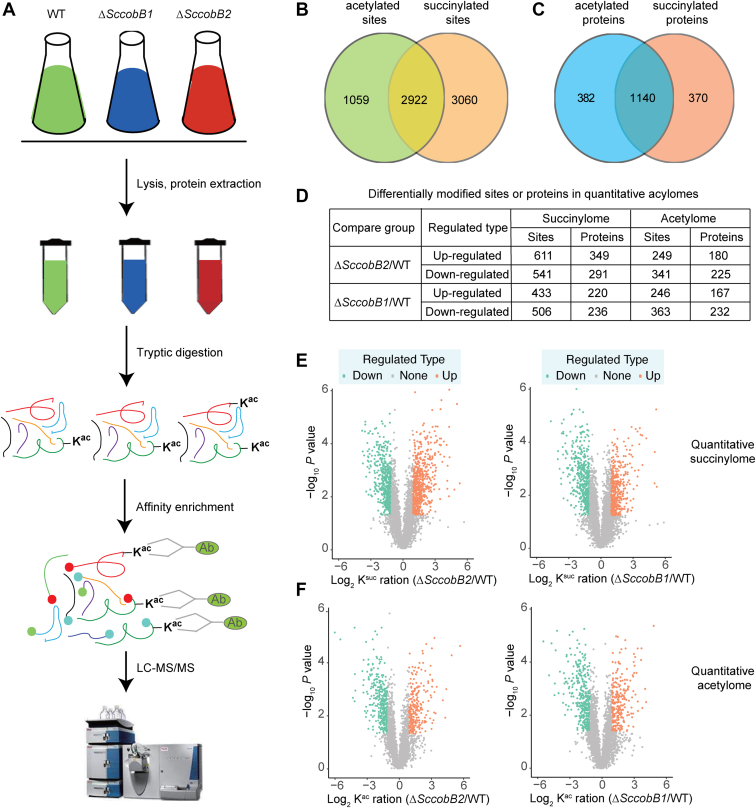
Fig. 5.
Quantitative acylome analyses after knocking out SccobB1 or SccobB2.A, schematic representation of the workflow used in quantitative acylome analyses. The quantitative acetylome and quantitative succinylome analyses were performed following the similar procedures (see Experimental Procedures section). Only the quantitative acetylome was shown here to simplify. B, the intersection of acetylated and succinylated sites in Streptomyces coelicolor proteomes. C, the intersection of acetylated and succinylated proteins in S. coelicolor proteomes (the bimodified proteins including those with acetylation and succinylation at separate sites in one protein). D, the summary number of the differentially modified sites or proteins in quantitative acylomes. E, scatter plot showed the details of changes in succinylated peptide intensities between the S. coelicolor wildtype and ΔSccobB2 cells (left) and between the wildtype and ΔSccobB1 cells (right). F, scatter plot showed the details of changes in acetylated peptide intensities between the S. coelicolor wildtype and ΔSccobB2 cells (left) and between the wildtype and ΔSccobB1 cells (right). When p < 0.05, the change of modification level >2 was deemed as upregulated significantly (brown dots), and the change modification level <0.5 was deemed as downregulated significantly (cyan dots).