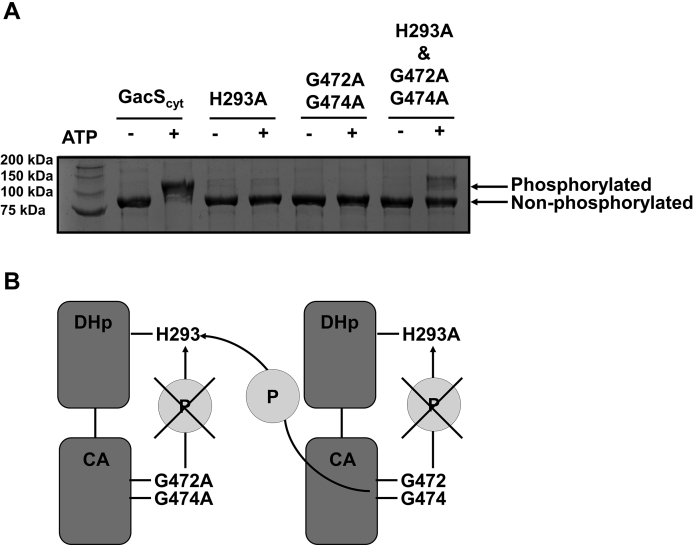
Figure 5.
GacS autophosphorylates in trans.A, an autophosphorylation assay followed by Zn2+-Phos-tag SDS-PAGE was used to examine the autophosphorylation of GacScyt and GacScyt variants in the absence and presence of ATP. GacScyt wild-type, GacScyt H293A (a variant that cannot undergo autophosphorylation), GacScyt G472A G747A (a variant that cannot bind ATP), and an equimolar ratio of GacScyt H293A and GacScyt G472A G474A were used to assess the ability of GacS to autophosphorylate in trans or in cis. GacScyt and the GacScyt variants are 77 kDa. Each lane contains 7.74 μg protein. GacScyt has three potential phosphorylation sites (the catalytic histidine in the DHp domain, the conserved aspartate in the receiver domain, and the conserved histidine in the Hpt domain). B, autophosphorylation assay. Individual variant constructs (GacScyt H293A and GacScyt G472A G474A) are unable to undergo cis autophosphorylation, but when both variant constructs are introduced into the autophosphorylation assay, they can autophosphorylate in trans. The histidine kinase region is shown for clarity even though the assay was performed with the cytosolic region of GacS.