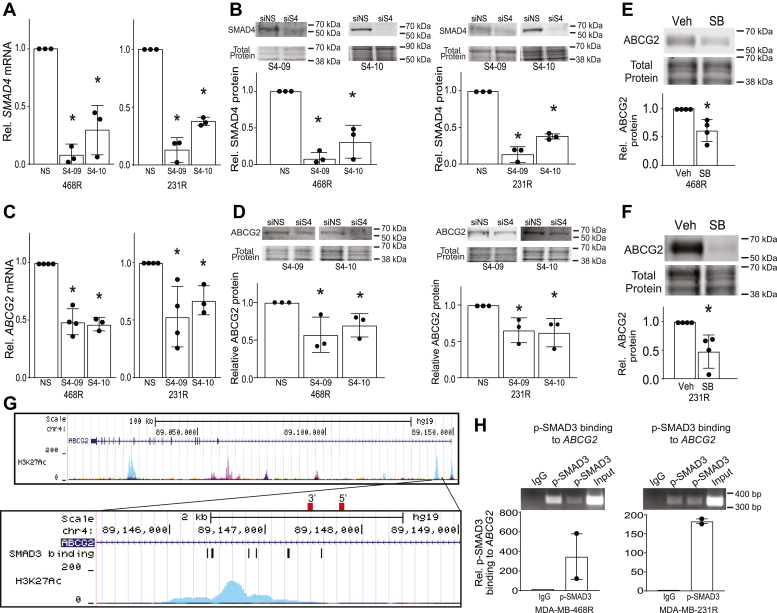
Figure 7.
TGF-β/activin signaling sustains expression of ABCG2 in CDK7i-resistant cells.A, quantitation of SMAD4 mRNA and B, protein expression in MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 in resistant cells after siRNA-mediated silencing of SMAD4 with two different siRNAs, SMAD4-09 (S4-09) and SMAD4-10 (S4-10), or transfection with a nonsilencing control (siNS). Quantitation of SMAD4 protein expression relative to total protein for the experiments in triplicate is shown in the lower panel. C, SMAD4 silencing reduces ABCG2 mRNA and D, protein expression in MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231-resistant cells. Quantitation of ABCG2 protein expression relative to total protein for the experiments in triplicate is shown in the lower panel. E, SB431542 (11.2 μM) treatment of resistant MDA-MB-468 reduces ABCG2 protein expression. F, SB431542 (5.6 μM) treatment of resistant MDA-MB-231 cells reduces ABCG2 protein expression. Quantitation of ABCG2 protein expression relative to total protein for the experiments in triplicate is shown in the lower panel. G, genome region depicting open chromatin as indicated by publicly available H3K27Ac ChIP-Seq data of the ABCG2 gene locus. The red rectangles show the positions of the primers used in the ChIP-PCR. H, p-Smad3 ChIP-PCR of a predicted binding site in the ABCG2 promoter regulatory region in resistant MDA-MB-468 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Error bars show the range of the p-SMAD3 binding as quantified by PCR from experimental duplicates. For all other data, error bars are means ± SD. ∗p < 0.05