Figure 4.
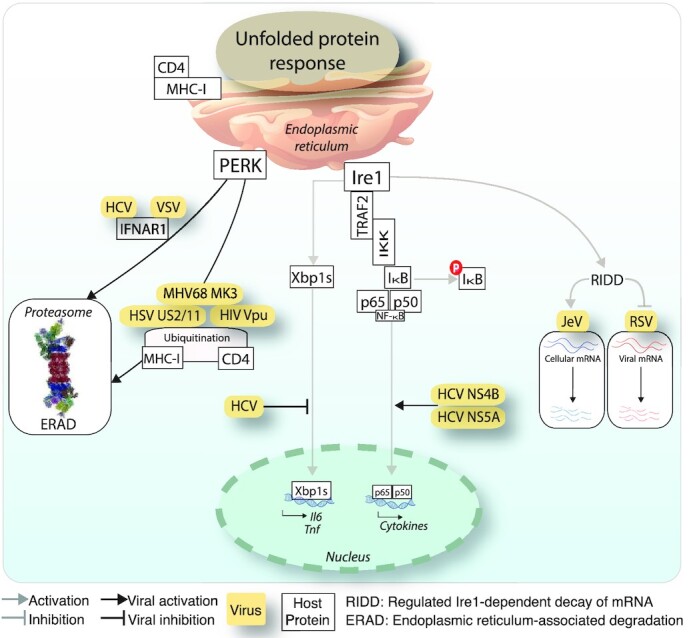
Viral modulation of innate immunity effectors interlinked with the Ire1 and PERK branches of the UPRER. Viruses intercept signalling from the Ire1-Xbp1 axis to innate immunity hubs by interfering with activated NF-κB or RIDD. This can trigger proviral effects by degradation of host mRNAs or raise susceptibility to antiviral effects, for example when RIDD degrades viral RNA. PERK signalling can be activated by viruses to target key innate immunity components, such as IFNAR1 or MHC-I for proteasomal degradation. Abbreviations: PERK, Protein kinase activated by double stranded RNA (PKR)-like ER kinase; Ire1, Inositol-requiring enzyme 1; TRAF2, TNF receptor associated factor 2; IKK, IκB kinase; CD4, Cluster of differentiation 4 glycoprotein; MHC-I, Major histocombatibility factor I; RIDD, Regulated Ire1-dependent decay of mRNA; JeV, Japanese encephalitis virus; RSV, Respiratory syncytial virus; ERAD, ER-associated degradation; IL-6, Interleukin-6; TNF, Tumour necrosis factor; HIV, Human immunodeficiency virus; HSV, Herpes Simplex Virus; MHV, Mouse gammaherpes virus; HCV, Hepatitis C virus; VSV, Vesicular stomatitis virus; IFNAR1, Interferon alpha or beta receptor subunit 1.
