Fig. 2.
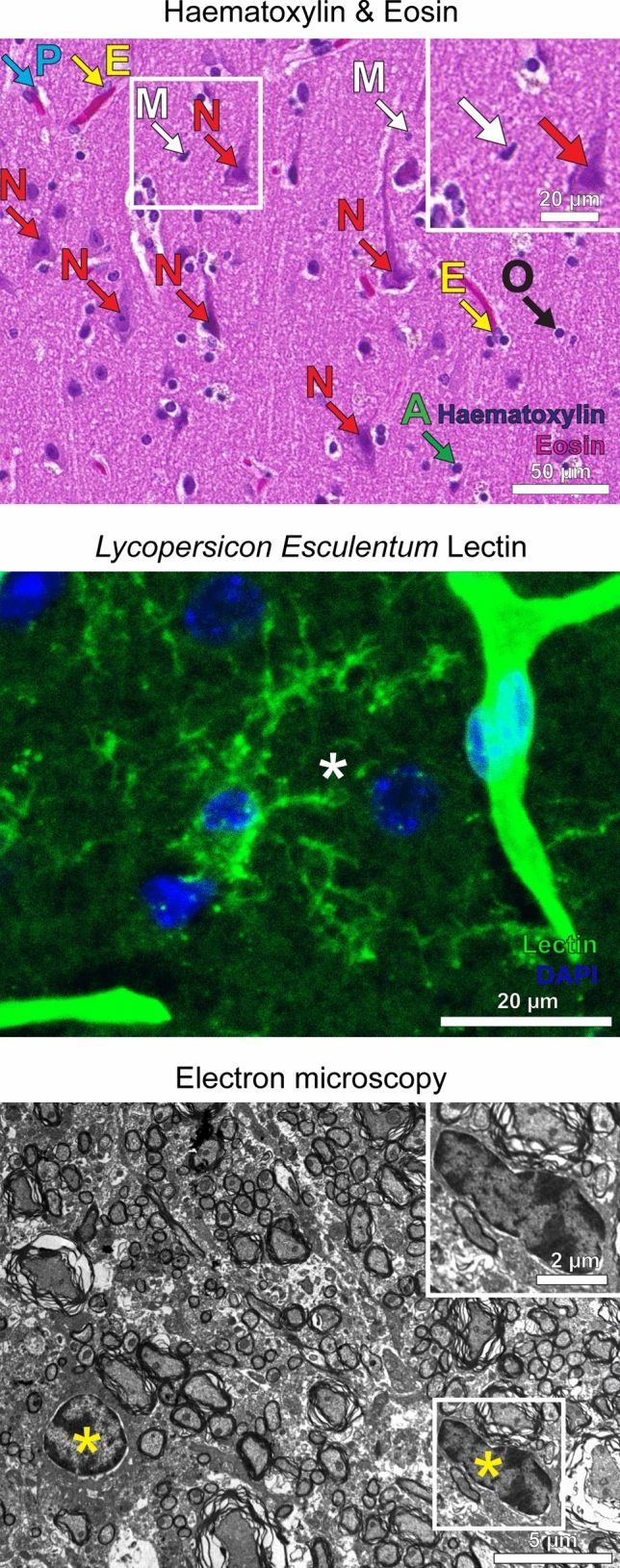
Visualization of microglia by using non-antibody-dependent staining techniques. a Different cell types including microglia can be identified in a Haematoxylin & Eosin section (H&E) of a healthy human cortex. Microglial nuclei (M) are small and dark, partially appear irregular and sometimes elongated with a “cigar-like” or “comma-like” shape. Perivascular macrophages (P) are located along blood vessels, in which endothelial cells (E) can be identified by their elongated nuclei. Arrows also point towards neurons (N), oligodendrocytes (O) and astrocytes (A). Scale bars: 50 µm and 20 µm (insert). b Lectins stain ramified microglia within the cortex of a mouse brain (asterisk). Cerebral vessels are stained as well (upper right). The staining with lectin (obtained from Lycopersicon Esculentum) is shown in green, DAPI in blue. Scale bar: 20 µm. c An electron microscopy image of a murine spinal cord is depicted. Microglia are typically small in size, partly have a “bean-shaped” nuclei (yellow asterisks) and only show little cytoplasm. Scale bars: 5 µm and 2 µm (insert)
